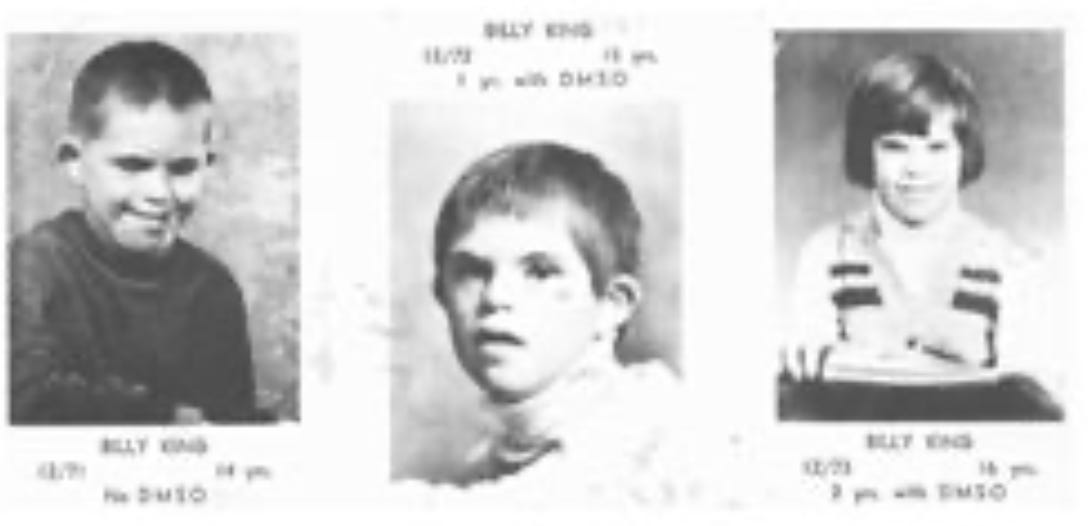The Evidence DMSO Could Save Millions From Brain and Spinal Injury
The decades of evidence showing DMSO revolutionizes the care of many "untreatable" circulatory and neurologic conditions.
Story at a Glance:
•DMSO is a remarkably safe chemical that protects cells from otherwise fatal stressors (e.g., freezing, burning, shockwaves, ischemia). Since the heart, brain, and spinal cord are particularly vulnerable to injury, DMSO can produce miraculous results for those conditions.
•The usage of DMSO completely transforms the management of strokes (including brain bleeds), heart attacks, and spinal cord injuries. As I will show here, had the FDA not sabotaged DMSO’s adoption, in addition to countless lives being saved, millions could have been protected from a lifetime of disability or paralysis.
•DMSO has many other remarkable properties. For example, it stabilizes proteins, and thus treats many challenging protein disorders (e.g., amyloidosis and numerous genetic disorders).
•Many conditions DMSO treats are typically considered to be incurable. In this article, I will focus on DMSO’s remarkable utility for the conditions that respond best to intravenous DMSO (e.g., a variety of circulatory disorders like varicose veins or Raynaud’s) and complex neurological disorders (e.g., Down Syndrome, Developmental Delay, ALS, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s), along with how to administer IV DMSO and DMSO stroke protocols.
If I were stranded on a desert island or knew the world was ending and I could only bring a few therapies with me, one of them, without a doubt, would be DMSO. This is because:
•It treats a wide range of severe illnesses which are often otherwise incurable and frequently fatal or lead to a lifetime of permanent disability.
•It effectively treats acute injuries and rehabilitates chronic musculoskeletal disorders (e.g., arthritis). Because of this, it’s one of the best “pain medicines” out there and has allowed many to get their lives back.
•It has a variety of unique properties that open up a completely different dimension to how medicine can be practiced.
•It is one of the safest medically active substances in existence.
Remarkably, in the 1960s, this was recognized and DMSO took the nation by storm (e.g., people everywhere were clamoring for it, gas stations would often advertise they sold it, and tens of thousands of research studies were conducted by enthusiastic scientists around the globe). Now however, outside of it being a laboratory chemical or an alternative therapy some people use for joint pain, few are even aware of DMSO’s existence.
This was due to the FDA waging a multi-decade long war against DMSO (despite widespread outcry from Congress and the public), which I believe was arguably the worst thing the FDA has ever done to the country.
Since I am uniquely positioned to present many of the forgotten sides of medicine to the public, I’ve long felt the DMSO story needs to be told. Simultaneously however, since there is a wealth of data on this topic, I wanted to ensure I honored the importance of this subject and accurately present it. For this reason, I’ve spent the last three months reading and arranging thousands of pages of literature. Since there is so much to say on this topic, this series will be broken into a few parts. In the first installment, I will cover the key properties of DMSO and the challenging conditions where it provides the most profound benefits.
What is DMSO?
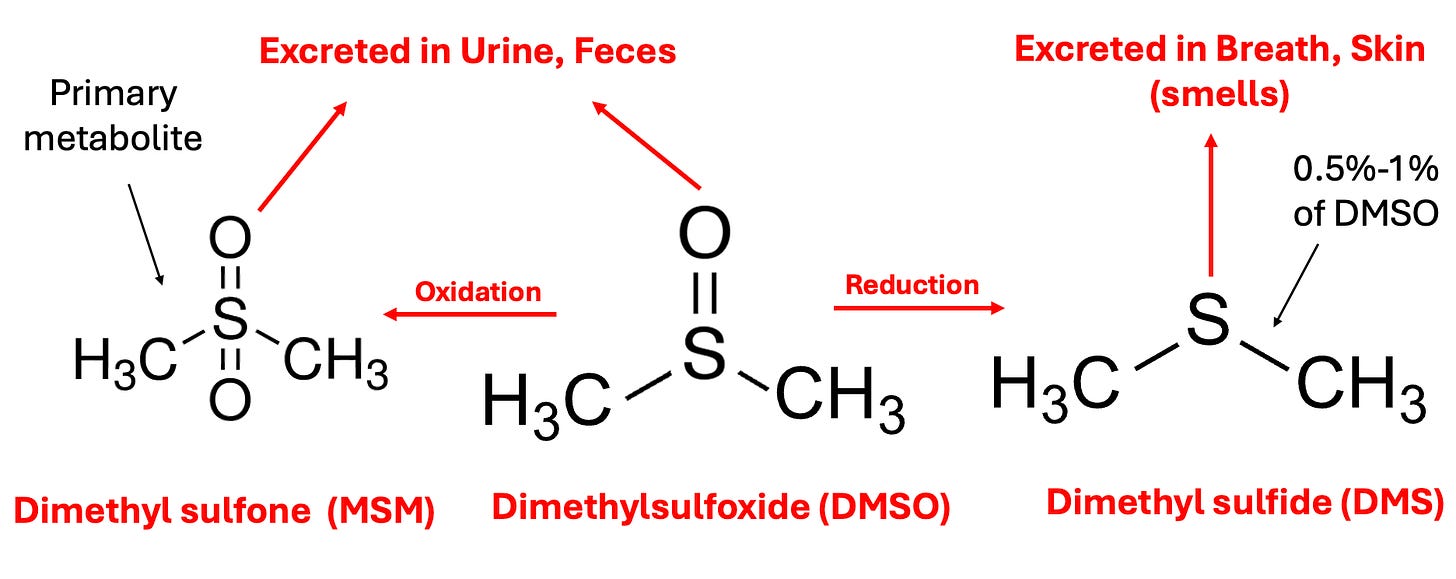
Dimethyl sulfoxide, as the name implies, is comprised of two methyl groups and an oxygen atom bonded to sulfur. This simple chemical and its breakdown products exist in nature (e.g., they can be found in small amounts in milk, tomatoes, tea, coffee, beer clams, and cooked corn, while the salty smell of the ocean is, in part, due to microalgae near the surface creating dimethyl sulfoxide—some of which also makes it into the rain).
In the body, DMSO is then oxidized or reduced, with the oxidized form (more commonly known by the name methylsulfonylmethanethe or MSM—a common joint healing supplement) being the primary fate of it, while the reduced form DMS (which naturally exists in trace amounts in the body) is the more notorious metabolite because it is responsible for DMSO’s characteristic “side effect,” a distinctive garlic or clam-like odor (or taste) that is excreted through the mouth and skin which certain individuals have difficulty tolerating (and forcing certain longterm DMSO users to creatively arrange their social life). This effect typically lasts a few hours, but in certain cases can last up to 72 hours, and appears to be reflective of the overall health of the body (since as people detox, their DMSO odor decreases).
Note: one school of thought in integrative medicine (e.g., Dr. Mercola is a strong proponent of this model) argues that insufficient oxidation, which leads to a build-up of reduced molecules in the body (termed reductive stress) is a root cause of many illnesses (e.g., the mitochondria cannot function properly if the electron transport chain is reduced). The susceptibility to the DMSO odor is one of the best illustrations I have found of this model, particularly since there are many reports showing that concurrently taking chlorine dioxide (an oxidizing agent) eliminates it (as does a user’s overall health improving over time). Likewise, some DMSO users and one study have found that when DMSO was taken at the same time as alcohol (another oxidizing agent), the odor was reduced, whereas when alcohol was given an hour after DMSO, the opposite occurred (which touches upon the fact DMSO can sometimes cause excessive drowsiness if combined with a sedative).
Due to its relatively small size, having both a polar and non-polar half, being able to form hydrogen bonds slightly stronger than those found between water molecules, and not releasing protons, DMSO has two remarkable properties:
•It acts as a near-universal solvent (e.g., it interacts with a vast range of biomolecules and can easily mix with any concentration of water).
•It’s able to pass through biological membranes without damaging them (something to my knowledge, nothing else can do).
Because of this, DMSO will rapidly enter the body (including the brain) regardless of its route of administration (e.g., within 5 minutes after going on the skin it can be found in the blood, and within an hour it can be found within the bones), but simultaneously does not accumulate within the body after prolonged use (and virtually none remains a week after administration).
Note: in one study of rats, radio-labeled DMSO was found to enter all tissues of the body within 30 minutes (with the highest levels seen in the plasma, kidney, spleen, lung, heart, and testes and the lowest in the lens of the eye), with DMSO levels declining to minimal levels after 24 hours, another study found over 90% of topically applied DMSO is absorbed with tissue concentrations peaking 1.5 to 2 hours after topical administration (and 85% being excreted unchanged in the urine after 24 hours) while another study found orally administered DMSO reached a peak blood level in 4 hours and was undetectable after 120 hours, while MSM appeared in the blood after 48 hours and disappeared after 400 hours (with another human study finding similar results).
Additionally, studies in mice and rats have shown that DMSO at 10–15% concentrations reversibly opens the blood-brain barrier (BBB), allowing proteins like horseradish peroxidase (HRP), drugs like pemoline or L-dopa (particularly when combined with carbidopa), drug carrying lysosomes, and amino acids like tyrosine to reach brain tissue in higher amounts than without DMSO.1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 This ability to facilitate drug delivery to the brain underpins DMSO’s therapeutic potential for neurological disorders. Likewise, DMSO has been shown to enhance the penetration of light into brain tissue, greatly improving optical diagnostic techniques (which have significant value in the treatment of certain neurologic disorders).
Note: there are mixed results on DMSO temporarily opening the BBB (e.g., these four studies found it did not1,2,3,4,5).
DMSO in turn, has an almost endless amount of uses as it can be applied in almost any manner (e.g., it is frequently applied through the skin—although less is absorbed in this manner than the other routes of administration). Almost any drug or substance can be combined with it and administered through the skin (e.g., steroids, NSAIDs, numerous antibiotics or antivirals, glucose, vitamin C, hydrogen peroxide, or chlorine dioxide). In many cases, the effect of those drugs is enhanced, and simultaneously, their toxicity is reduced (although, in some cases, the toxicity increases).
Note: DMSO is less effective at bringing larger molecules into the body (e.g., it had been hoped it could be mixed with insulin so diabetics could have a way to bypass the need for injecting insulin—but this didn’t work).
Cellular Protection
DMSO’s ability to spread throughout the body (including into the brain) initially seems concerning—however rather than be toxic to cells, DMSO heals them and protects them from damage and a wide range of otherwise lethal stressors. Since DMSO does not expand when it freezes (at 65.4°F), this property (and the fact that a 66% DMSO 33% water mixture freezes at -99.4°F), has made it a revolutionary substance for preserving frozen cells (e.g., stem cells). In contrast, very few other substances exist that cells can tolerate such a high concentration of.
Note: since some of the information I need to present here is a bit technical for those wanting more references, if you find some of the information is too dense, skip over it. Additionally, I need to acknowledge many of these experiments were cruel and go against my own values of supporting animal welfare.
DMSO, in turn, has been shown to:
•Protect tissue from dying when its blood supply is cut off (e.g., in skin flaps, in the kidneys,1,2 in the small intestine, in the liver, or in the heart—particularly when hydrogen peroxide is given concurrently as an oxygen donor), prevent a reperfusion injury when its blood flow is restored, prevent the formation of clots when blood flow is restored (e.g., in mesenteric veins), reduce the amount of permanently damaged tissue following a myocardial infarction, reduce tissue carbon dioxide (and raise tissue oxygen if combined with H₂O₂) and maintain the heart’s ability to circulate blood when its blood supply is cut off.
•Prevent a rapid influx of calcium or sodium ions, a process which frequently occurs when a cell’s viability is threatened (and then results in the death of the cell). Likewise, DMSO reduces the activity of caspase proteins (which trigger cell death) in the liver, heart, and airway epithelial cells and to suppress glutamate induced-excitotoxicity (a common source of nerve cell death).
Note: in two studies where rat hippocampal slices exposed to glutamic acid, DMSO significantly improved the neuron’s return to normal firing and strength, with 66.7-82.3% of them recovering.1,2
•Prevent heart damage caused by dietary copper deficiency and kidney failure caused by toxic mercury exposure.
•Protect animals from organophosphate exposure1,2,3 (including lethal dose of nerve gas) and to treat snakebites in dogs.
•Increase the production of ATP in cells, and to produce it when energy production has been compromised (e.g., minute concentrations of DMSO have been shown to increase metabolism by shunting metabolites from glycolysis to the mitochondrial Krebs cycle or to make a part of the mitochondria able to synthesize ATP without the rest of the mitochondria being present1,2,3,4). For example, DMSO increased the metabolism of pyruvate and glucose in brain slices and in a study where mice were decapitated, DMSO prolonged how long the mice continued to gasp (breathe) and hence how long brain function continued.
•Prevent asphyxiation from being lethal (e.g., one study put rats into a pure nitrogen environment for 210 seconds, and found that 90% who received DMSO in advance survived compared to 15% of those that received saline).
•Protect cells from being destroyed by sonic disruption via an ultrasonic vibrator (with 78% of cells receiving 10% DMSO surviving compared to 13% of controls).
•Protect plants from dehydration and osmotic stress (which has also been shown in many other organisms).
•Save the fingers of individuals with severe frostbite that would otherwise require amputation. DMSO has also been shown to protect cells (and DNA) from freezing damage,1,2,3 to protect wheat seedlings from cold, and in multiple studies, to protect rabbit ears and thighs from being damaged by frostbite induced by immersion in a -42°C bath.1,2,3
Note: one of the most common uses for DMSO is to preserve cells being frozen—for example DMSO protected brain and pituitary tissue losing cellular receptors after being frozen and thawed. In turn, thousands of studies (which are beyond the scope of this series to cover) have demonstrated both that DMSO protects cells from damage when being frozen and that the viability of cells is maintained while in high concentrations of DMSO for prolonged periods (indicating DMSO is fairly non-toxic to cells).
•Treat a variety of burns (e.g., superficial burns or partial thickness burn wounds) without being prone to producing infections (e.g., a 1985 study by Russian burn specialists, in adolescents, found DMSO was superior to the other treatment options [nitrofurazone, trimecaine, and monomycin] while another study also found DMSO prevents burns from becoming infected). This includes severe acid skin burns (along with preventing their progress), and both acidic and alkaline burns that erode the esophagus (e.g., by inhibiting the destructive inflammatory response following those esophageal burns) or alkali burns to the eye.
Finally, a study of 1371 patients with skin disorders (including 173 patients with second or third-degree burns on the hands, feet, and legs) who received a topical DMSO spray approximately three times a week found that 95.04% had a complete recovery, with the majority of the remaining 4.96% being due to premature cessation of DMSO or the patient no longer being under observation.
Note: a dog study showed DMSO also aids in the elimination of damaged (burned) skin.
There are also countless cases of severe burns that within minutes of DMSO stopped hurting (a major problem with burns), didn’t blister, and subsequently fully recovered (e.g., no skin contractures). One of the most extraordinary ones (reported by William Campbell Douglass) involved six year old girl who’d slipped her index finger in a light socket for a prolonged period, after which it was cooked through and burned ash white at the tip. Within 30 minutes Douglass got the finger into a full-strength DMSO bath, and after 20 minutes, the searing pain had disappeared, the next day the finger turned pink, and then rather than be lost, fully recovered.
In practice, provided DMSO can administered quickly enough, it will prevent injured (burned) tissue from dying, a property that is repeatedly seen with DMSO various applications (e.g., through it rescuing neurons after a stroke).
Note: patients have also reported DMSO relieves sunburns in 10-30 minutes.
•Protect cells (including in a prophylactic manner) from being damaged by (often otherwise fatal) radiation exposures.1,2,3,4 For example, DMSO prevented X-ray damage to hamster ovary cells (by accelerating DNA repair), and to prevent the harmful (bystander) signals irradiated cells emit in their vicinity from damaging non-radiated cells (a fascinating phenomenon which I believe is mediated through mitogenic radiation) along with protecting certain bacteria from x-ray exposure (also shown in this and this study). Likewise, DMSO has been repeatedly shown to reduce chromosome damage from radiation1,2 and prevent radiation from creating harmful free radicals.
Note: low doses of DMSO have also been shown to protect nerve fibers from UV radiation.
•Protect living organisms from radiation exposure.1,2 For example, DMSO pretreatment prior to a lethal radiation dose fully protected mice (along with protecting their stem cells), protected monkeys and dogs (increasing survival by 75%), protected dogs and against radiation-induced intestinal damage, protected monkeys against radiation-induced bone marrow damage, and rabbits (along with protecting their lungs from severe injury).
Likewise, numerous reports showed applying DMSO to newborn rat skin protected them from damage from x-ray exposure, while in fruit flies, DMSO significantly reduced x-ray mortality and mutations of their sperm and in golden hamster embryos, DMSO protected them from gamma rays—the strongest form of radiation. DMSO has also been shown to cataract formation in mouse eyes following radiation exposure.
Note: DMSO has also been found to prevent damage from radiation therapy in non-cancerous cells and thus has been used as complementary cancer treatment.
•Reduce oxidative stress1,2 and neutralize harmful free radicals (e.g., those caused by radiation like hydroxyl) through scavenging charged ions (e.g., H+) alongside forming protective DMSO radicals. This, for example, was shown to be a mechanism behind DMSO’s ability to protect DNA from being damaged by radiation and one study found DMSO prevented 80% of the DNA damage caused by gamma radiation and 100% of the DNA damage caused by a free radical generating system (which used iron and hydrogen peroxide). Likewise, trace amounts DMSO protects plants from ozone gas injury and to counteract reactive hypochlorous acid, superoxide, hydrogen peroxide (but simultaneously also works synergistically with oxidative therapies and does not affect neutrophil viability).
Note: many microrganisms reduce or oxidize DMSO as needed (e.g., for metabolism or protection). For example, DMSO reduction in marine phytoplankton was increased 3 fold under high irradiance.
Finally, due to these protective qualities, DMSO’s toxicity is extremely low (e.g., due to the immense scrutiny DMSO has been subject to, a large number of animal safety studies were conducted, and in these, animals survived extraordinarily high doses of DMSO). Many human studies have also been done, the most significant of which involved 78 prisoners over the course of 14 and then 90 days applying 1 g/kg to their skin (over 3-30 times the maximum amount of DMSO typically used) and then being subject to an extensive battery of toxicology tests—all of which showed DMSO was safe. In turn, despite millions of treatments having been given, no death has ever been linked to DMSO (and the only two ever considered, one in 1965, and one in 1994 did not make a strong case DMSO was the cause of death).
Note: thousands of papers have been published on the biological effects of DMSO and I have not yet found one that reported an adverse event from DMSO. Because of that, I’ve mostly avoided mentioning each study I site here, “detected no adverse events from DMSO.”
Along with the garlic breath, the most common side effect (affecting 50-75% of users) is (reversible) irritation at the site when 70% DMSO is applied topically on the skin (which can be mitigated by applying a lower concentration of DMSO and frequently decreases with increasing topical application), that occasionally after prolonged used can lead to minor reversible changes in the skin (e.g., scaling). In roughly 15% of patients this skin reaction is marked and in 3.5% it is significant enough that they stop treatment.
Less common side effects include nausea, increased urination, sleepiness, and difficulty tolerating high IV doses. The most consequential (but fairly rare) side effect is an allergic reaction to it (which affects roughly 1 in 2000 users—although it does not ever seem to manifest in an anaphylactic fashion). Additionally, there is a high theoretical risk of a poison being on the skin when DMSO is applied and brought into the body (hence why patients are advised to wash their skin before applying DMSO) but significant instances of this have been extraordinarily rare despite millions of DMSO treatments being performed (rather the more common issue arises from using incompatible IV tubing which DMSO can dissolve as it travels to the body). Lastly, it is generally advised not to inhale DMSO (although it rarely vaporizes).
Circulatory Disorders
In addition to protecting tissues from death, DMSO is remarkably effective at removing excess fluid from outside the bloodstream, increasing circulation, and eliminating circulatory obstructions (e.g., clots). As each of these issues comes up quite frequently, DMSO is often extremely helpful in a variety of circulatory disorders.
For example, the leading DMSO researcher found that 50% of patients with Raynaud’s syndrome had their symptoms eliminated with DMSO and that thrombophlebitis responds excellently to DMSO and two researchers, using plethysmographic methods, demonstrated objective improvement in peripheral artery insufficiency in a large number of patients receiving topical DMSO . Likewise, DMSO has been shown to improve diabetic circulatory impairments such as peripheral neuropathy, or diabetic ulcers (where one study of hundreds of patients reported over a 94% treatment success rate) and prevent future amputations.
DMSO (topically and especially intravenously) is also quite helpful for varicose veins, in some cases improving the varicose veins within minutes and having the wiggly veins not reappear for months, which has been hypothesized to result from DMSO strengthening the vessel walls and their tone alongside generally improving venous and capillary circulation. Likewise, a study of 67 patients with varicose ulcers (39 females and 28 males), found they had a remarkable response to DMSO (even chronic ulcers which had been present for years and not responded to other treatments).
Additionally, DMSO has been shown to help many other circulatory disorders:
Note: another DMSO study found that of 57 patients with peripheral vascular diseases, 35 had a complete remission of symptoms, 10 had a partial remission, and 12 had no response.
This is likely because, in addition to the previously mentioned properties:
DMSO can also increase or decrease the force of heart contractions (e.g., a 70 mM DMSO concentration or less has a positive inotropic effect, while a higher one can do the opposite or create a mild hyperpolarization that prolongs the action potential) in a manner independent of beta-adrenergic receptors, and does not alter cardiac rhythm. A slow infusion of DMSO can also cause a reduction of systemic vascular resistance and an increase in cardiac output (which was also shown in this study that simulated a heart attack).
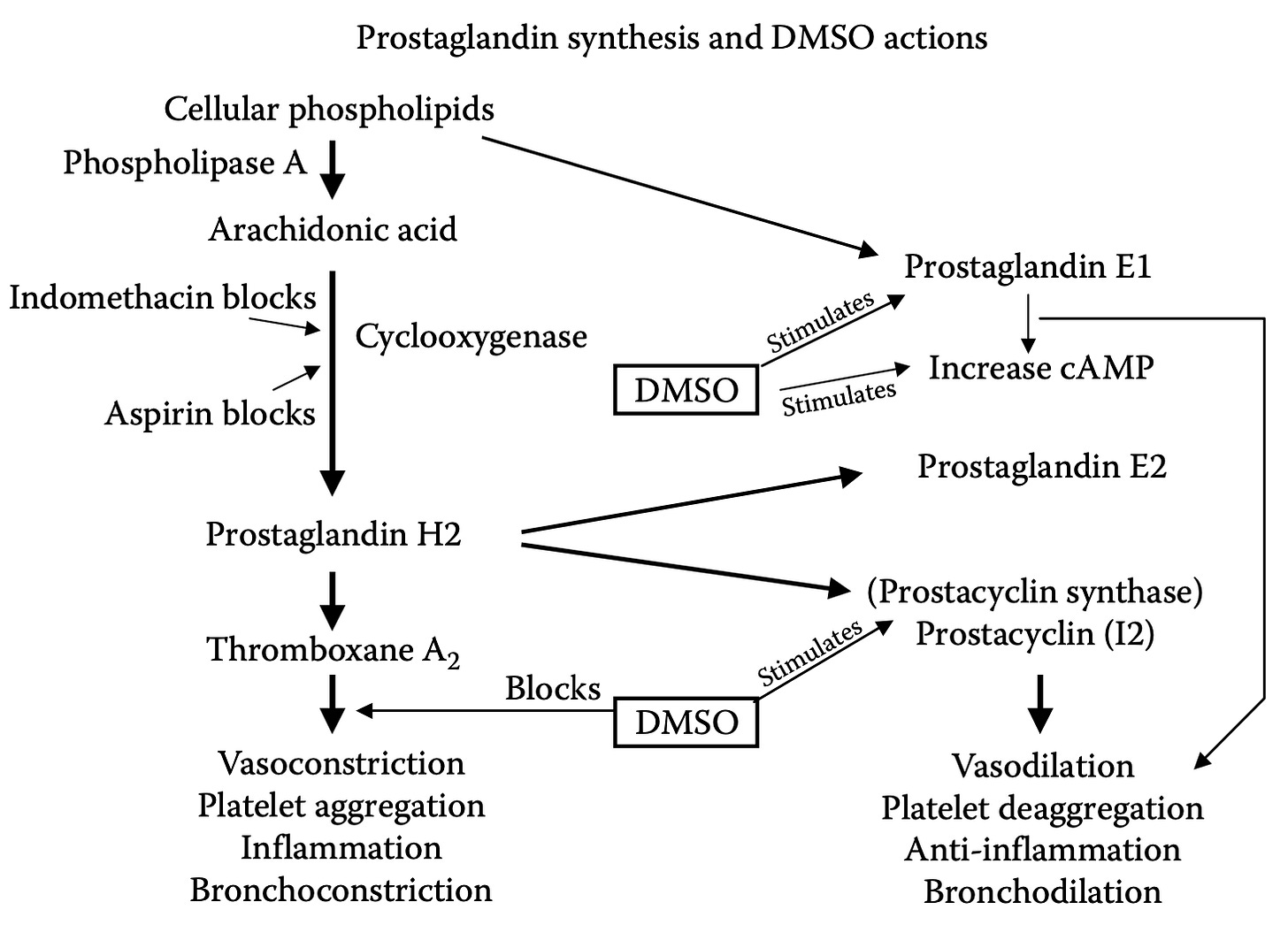
DMSO prevents blood clot formation in the body and is a powerful platelet deaggregator (which prevents clotting). For example, DMSO was found to reverse the reduction of coronary blood flow induced by a critical stenosis on the canine [dog] circumflex coronary artery without changing their other circulatory parameters, it’s been shown with electron microscopy that DMSO prevented clots from forming at surgically blocked carotid arteries and DMSO and as this review shows, DMSO has a diverse number of ways reverses brain injuries caused by an interruption of blood flow (which predominantly affect prostaglandins, thromboxanes and platelets).
Note: DMSO has been shown to treat multiple sclerosis (detailed here). When myelin is broken apart by the immune system, phospholipids within the debris that can cause blood clotting become exposed and compromise the critical blood supply nerves rely upon, providing a secondary mechanism to explain the neurodegeneration seen in MS. Existing anticoagulants do not target this clotting pathway, but a very interesting Russian study determined that DMSO inhibited the blood clotting triggered by myelin in a dose-dependent manner.
DMSO’s effects on platelets are thought to be because:
•DMSO is a sulf-hydryl inhibitor (which platelets need to bond) and a hydroxyl radical scavenger (which also inhibits platelet function).
•DMSO inhibits tissue factor (TF) expression (a key part of clot formation—especially in the presence of TNF-α), thrombus (clot) formation, and vascular smooth muscle cell activation. TF (a platelet protein) is a key link between inflammation and blood clotting.
•It increases cAMP (cAMP inhibits platelet aggregators) by inhibiting one or more of the platelet enzymes that breaks cAMP down (PDE2, PDE3, and PDE5—which is how many circulation improving drugs like Viagra also work, along with certain cognitive improving ones).
•It is a selective inhibitor of COX-1, it stimulates PGE1, and inhibits PGF2α, blocks PGE2 synthesis and likely blocks the release of thromboxane A2.
Furthermore, DMSO significantly inhibits platelet adhesion and aggregation induced by single agents (e.g., ADP, epinephrine, arachidonic acid, collagen, or platelet-activating factor) in a dose-dependent manner, with higher concentrations showing stronger suppression.1,2
These effects are fully reversible upon washing, suggesting DMSO’s safety for clinical applications.1,2,3,4 For example, at a 3% concentration, DMSO reduced platelet adherence, aggregation, and recovery from hypotonic shock in vitro compared to control and washed platelet groups, with these protective effects also being reversible.1,2,3 Additionally, DMSO temporarily reduces serotonin uptake by platelets and impairs their ability to degranulate and release serotonin, a key amplifier of clot formation, thus further reducing clotting.1
Note: Since PRP’s therapeutic effect relies on platelet activation and aggregation at the injection site, combining DMSO with PRP in a single local injection may reduce PRP’s efficacy in that context.1,2,3
Lastly, in a Phase 1 dose-escalation safety trial, transfusion of DMSO cryopreserved platelets in patients with severe thrombocytopenia and active bleeding showed no abnormalities in coagulation (such as increased clotting or bleeding), suggesting that DMSO-preserved platelets and possibly DMSO infusions are safe in patients at high-risk of bleeding.
Note: in another study, DMSO inhibited platelet activation during freeze-drying by reducing the expression of two key activation proteins involved in aggregation (CD62p and PAC-1), while preserving normal platelet aggregation responses.
In short, DMSO provides a variety of anti-clotting activities which are similar to (but eclipse) the effects of aspirin and unlike aspirin, does not have any associated adverse effects, which leads to a remarkable number of potential uses for it (e.g., incorporating it into a drug eluting coronary stent). These charts in turn tie together much of the above:
Note: a review paper on this entire subject can be read here.
Heart Attacks and Blood Vessels
Given all of these protective and circulatory enhancing properties, DMSO appears to be an immensely promising treatment for heart attacks. Unfortunately, relatively little research exists in this area and likewise, a situation where it could be done does not frequently come up (e.g., by the time you start chest compressions it’s unlikely you’ll also be applying DMSO). Nonetheless, I have had colleagues who have cases of having successfully treated heart attacks with DMSO (or a zeta potential enhancing regimen).
In turn, most of the research that’s been done in this region has not happened in humans, but rather through stimulating a heart attack (e.g., by temporarily cutting off the blood supply in an animal’s coronary artery), and in all of those studies (detailed here), the resulting damage to the heart was greatly reduced and in many cases, the heart partially retained its ability to pump blood. Likewise, other studies tested the heart’s response to a variety of other severe injuries—all of which found DMSO exerted a similar protective effective.
Note: this 2009 review paper extensively discusses the mechanisms through which DMSO treats cardiac and central nervous system damage.
Furthermore, since the health of the heart (and the likelihood) of a heart attack is highly dependent upon the health of vasculature, it is noteworthy DMSO also heals the blood vessels:
•In experiments with rat aortas and dog basilar arteries, DMSO, a reducing agent, inhibited and reversed vasoconstriction induced by oxidizing agents (e.g., peroxide, silver nitrate).1,2 Likewise, in rats, DMSO had a dose dependent vasodilatory effect on rat aortas (42.3-99,2% dilation) and in renal arteries (80.5-81.2%). Blocking voltage gated potassium channels partially prevented this dilation, suggesting DMSO acts upon these channels.
•DMSO at 10% induced a hormetic-like response characterized by increased intracellular ROS and redistribution of nitric oxide into cell-bound membrane vesicles, along with enhanced vesicle movement, displacement, and aggregation on endothelial cells. These changes suggest a potential role in modulating endothelial signaling and vasodilation capacity through vesicle-mediated nitric oxide release.
•A study attempted to model atherosclerosis by overloading rabbits with dietary cholesterol. It found that oral DMSO reduced the eventual atherosclerosis by 30-40% and halved the accumulation of cholesterol in the tissues.
•DMSO supported the growth of early blood and vessel-forming cells by promoting the development of human embryonic stem cells into endothelial, heart, and blood cell precursors.
•In human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVEC), pretreatment with 2.5% DMSO reduced TNF-α induced neutrophil adhesion, suggesting DMSO reduces blood vessel inflammation and atherosclerosis. In another study, DMSO inhibited programmed cell death in nutrient-deprived HUVECs by promoting DNA replication and enhancing cell survival. In a third study, DMSO protected HUVECs under oxidative stress by increasing HO-1, a protein that helps protect cells from harmful iron compounds, and by reducing programmed cell death through activating several anti-inflammatory and cell-protective pathways.
Current Stroke Management
Roughly 3.1% of adult Americans have experienced a stroke (a figure I expect to rise from the COVID-19 vaccines). Each year, this translates to about 800,000 people in the United States having a stroke, and in 2022, 165,393 died (making it the fifth most frequent cause of death in the United States), with between 20-40% of survivors experiencing long term disability from the stroke.
Because of the harm strokes pose to society, and the rate at which brain tissue deteriorates once its blood supply is lost, the medical system emphasizes doing everything that can be done to identify and treat strokes as soon as possible.
Unfortunately, different types of strokes exist. In most cases, the blood supply is cut off due to something (e.g., a clot) blocking the artery (an ischemic stroke). However in 13% of cases it’s instead due to a blood vessel rupturing and leaking out. This is problematic because the primary treatment for strokes is to inject a powerful clot busting medication (tPA) but in cases where the stroke is coming from a bleed, this can be disastrous. As a result, nothing can be done until the patient is accurately diagnosed (which requires a brain CT scan at the hospital), which in turn results in an even longer delay before tPA can be used to save a patient’s brain tissue.
Note: there are a few diagnostic signs that are more suggestive of a hemorrhagic stroke (e.g., a severe headache or unusual neurologic symptoms), but to our knowledge, no reliable method besides a CT scan exists to differentiate the two.
Worse still, the statistics on tPA (approved in 1996 and still the only FDA approved treatment for ischemic strokes) aren’t actually that good. Presently, tPA is only approved to be given within 3 hours of a stroke starting (as its likelihood of benefitting a patient decreases with time)and in practice, it is often given up to 4.5 hours after symptoms start (since some degree of benefit still exists).
When that window is met (which only happens about 25% of the time and ultimately results in roughly 1.8%-8.5% of ischemic stroke patients receiving tPA), the existing data shows that only 13% percent of patients who receive tPA significantly benefit from it (39% return to normal, compared to 26% who would return to normal without treatment), with an additional 19% of tPA users experiencing some degree of improvement (but not a full recovery) from it.
Worse still, tPA can cause significant bleeding, which is sometimes minor (e.g., gum bleeding), but also carries a 6.4% risk of a symptomatic brain bleed, and a 1.6% risk of a serious systemic hemorrhage (along with other issues such as a 1.3% to 5.1% risk of angioedema and tPA frequently causing reperfusion injuries). In turn, many risk factors exist for the increased bleeding (e.g., a few common risk factors can lead to a 33% chance of tPA causing a fatal bleed), and there have been many lawsuits for either giving or not giving tPA to a stroke patient. Additionally, tPA is a poor choice for larger obstructions (e.g., one within the internal carotid artery), which instead must be physically removed. In short—many ICU doctors I know are quite hesitant to use tPA as they have seen cases where it dramatically improved patients, many where it did not do anything, and quite a few disasters (especially in the early days of the therapy where it was used for heart attacks and then often caused the patient to have a fatal or debilitating brain bleed).
Note: the best data exists for tPa being injected directly into the obstructed artery with interventional radiology. Unfortunately, while many premier institutions offer this, it is a specialized procedure that is not available at most hospitals.
Finally, there is essentially no therapy for recovery from stroke—which in short explains why stroke is the second leading cause of death and the third leading cause of disability worldwide.
In turn, it would be paradigm shifting if an effective stroke therapy existed which:
•Effectively treated ischemic strokes.
•Had no risk of worsening a hemorrhagic stroke.
•Could easily be taken at home, and more importantly, be quickly given on ambulances.
•Protected brain tissue from dying.
•Prevented reperfusion injuries.
•Healed damaged brain tissue after a stroke.
I have been in health chats where twice now, folks were in the chat and were having a stroke, they both had DMSO on hand & took it, both strokes were stopped within 10-15 min and any damage was.
The fact that it’s been known DMSO does all of that for over 50 years (it’s even therapeutic for hemorrhagic strokes and can cross the blood-brain barrier to heal damaged neurons), in a nutshell, summarized why quite a few people I know harbor great animosity towards the FDA.
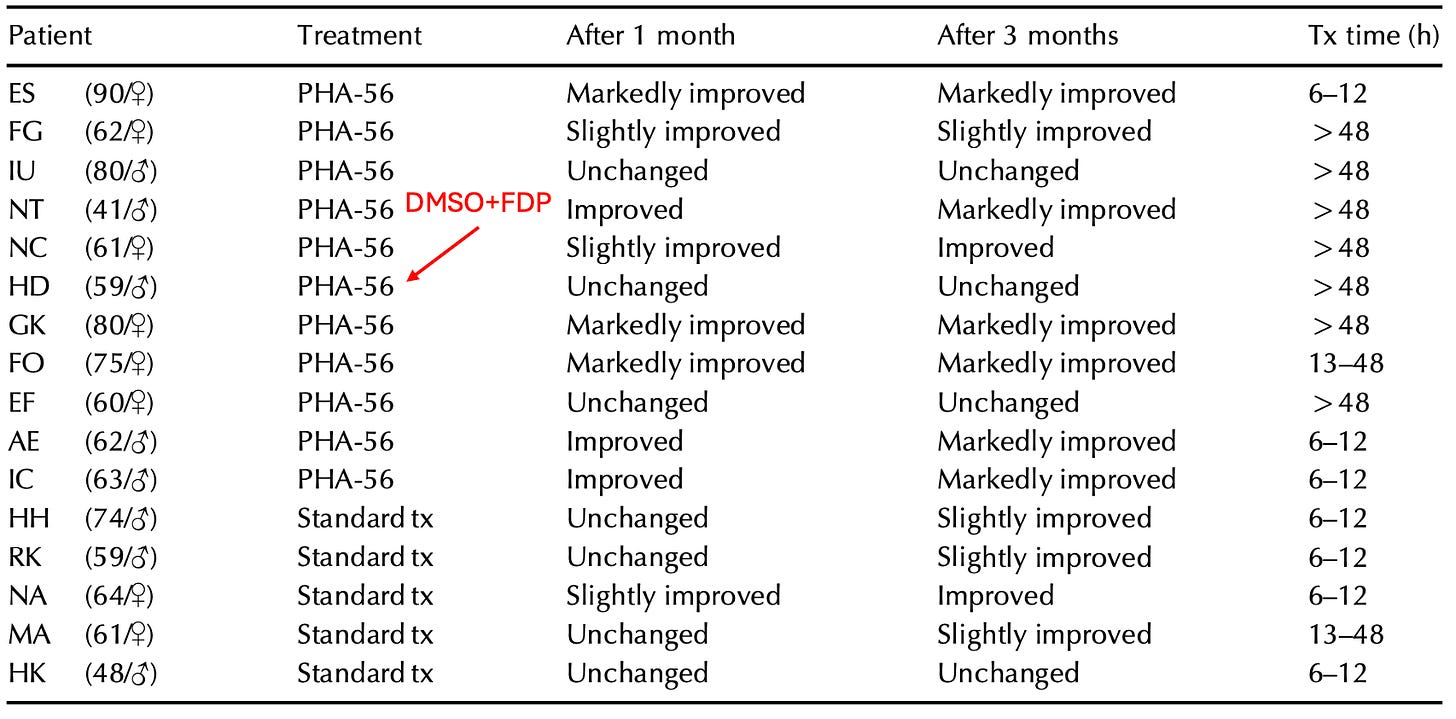
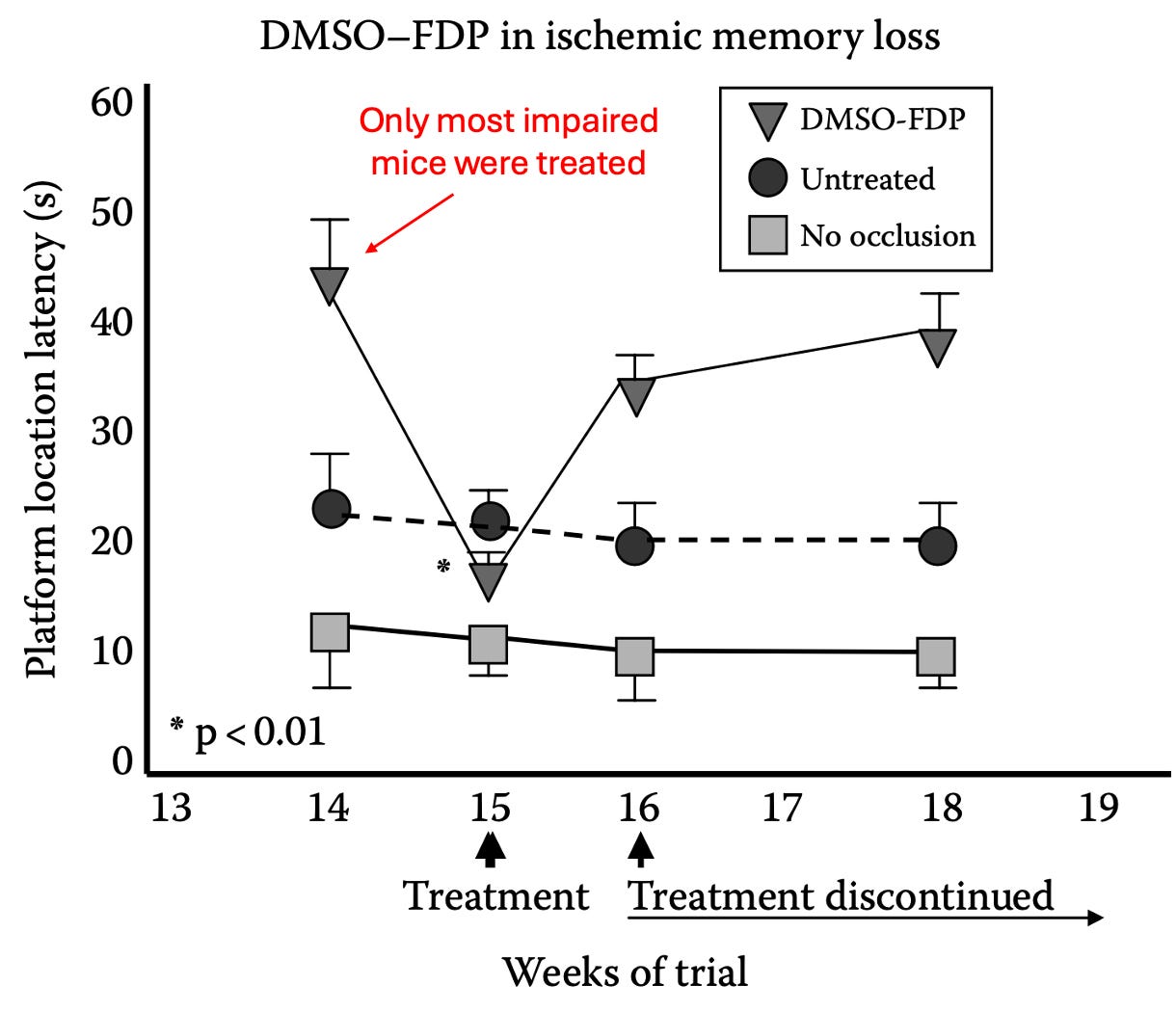
For example, a 2002 clinical trial (which can be viewed here) was conducted where DMSO and FDP (fructose diphosphate, a metabolite which cells turn into energy through glycolysis) mixed in 5% dextrose was administered intravenously twice a day (averaging 12 days) to 11 patients (average age 65) who presented with an acute or subacute ischemic stroke. After being subject to an extensive series of tests, it was concluded that DMSO was well-tolerated, that it benefited patients if given with 12 hours of symptom onset, and that 63% of the patients achieved 'improved' or 'markedly improved' neurological status (whereas for the patients receiving standard treatment, only 20% achieved an “improved” status three months later.
Note: since older patients are the most vulnerable to strokes and have had such a significant recovery (without adverse reactions), this indicates DMSO is an even more promising therapy for younger patients with strokes.
One of the most important aspects of this trial was that while DMSO is the most helpful when given immediately after a stroke, the trial showed DMSO could save the neurons long after the stroke had happened.
Given the existing options for strokes, a trial like this should have been immediately replicated by premier institutions around the world—but instead almost no one even knows it happened.
Additionally, there are also animal studies on the DMSO-FDP mixture:
•In a rabbit study, blood flow to their brains was cut off (via hypoxemia, hypotension, and a bilateral common carotid artery occlusion), which eventually caused them to develop isoelectric (flatlined) brainwaves. After 5 minutes of no brain activity, they received either DMSO and FDP or saline, and then after roughly 2 minutes had their blood supply restored (with the DMSO group having an extra 1.4 minutes of no blood flow). The DMSO group regained brain activity much faster (a result frequently seen in animal experiments), all survived and all had minimal brain tissue damage, whereas only 22% of the saline group survived (and were severely disabled with significant brain tissue damage).
•In a mouse study (which can be read here), mice were subjected to moderate or severe head impacts and then treated 5 minutes later with various compounds, then evaluated for motor function (via a grip test), brain tissue damage, and survival. DMSO-FDP was the most protective, DMSO the second best, while the rest (e.g., FDP alone) did not provide a benefit.
Ischemic Strokes
After I learned how unconscionable the FDA’s prohibition against DMSO was, I made a point to begin telling people (e.g., friends, relatives, patients) I felt were at risk of a stroke to stock DMSO at home, and since then, I’ve had instances where someone (or their caretaker) called me up, described a stroke, I gave them instructions on what to do (since they already had DMSO at home), and by the time they got to the ER, the stroke was “resolved” and in some cases, the ER was confused by the CT scan because it both looked like a stroke had happened and simultaneously that one had not.
Note: in my opinion, IV DMSO would have been ideal (and more effective) in those situations, but in each case, it was not feasible to implement.
Likewise, many compelling cases have been recorded of individuals who treated their strokes with DMSO:
A Los Angeles school teacher had a major stroke shortly after the start of the Christmas break. She was unconscious on her living room floor. DMSO treatment was started immediately after the stroke. The DMSO was first applied topically to her head within minutes of the stroke. Less than one hour after the stroke she was given DMSO by intramuscular injection. This patient was never taken to the hospital for this stroke. A prominent surgeon who was a family friend told the husband of this patient that it was important to keep her out of the hospital. The surgeon said that even though the treatment was completely legal, it would be difficult to get approval to give the DMSO especially by injection at his hospital.
This patient made a dramatic recovery. She regained consciousness later in the day in which she had her stroke. Treatment continued for the next week. Each day she received two topical applications of DMSO, one intramuscular injection of DMSO, and two doses of one teaspoonful of DMSO in juice. Her condition improved each day. When school resumed after the first of January, this teacher was back in the school teaching the students as if nothing had happened during the Christmas vacation. She never even mentioned it to the other people at the school. She continued teaching until she retired. She retired healthy with no disability.
Note: small strokes can still cause significant long-term issues (which DMSO often completely prevents), so as a general rule, I advise using DMSO anytime someone has a suspected stroke. Additionally, if you drive someone to the ER (and call in ahead to let the ER know you are coming), you have numerous opportunities to administer DMSO prior to placing the patient in the ER without delaying their care there (e.g., emergency brain surgery for a hemorrhagic stroke).
A lady was in a coma in a convalescent hospital and had been in the coma since her stroke three months ago. She was given little chance of recovery and was expected to remain in a vegetative state until her death.
When I first observed this lady, there was no response to any type of stimulus. She was alive, but appeared lifeless. It was decided that her treatment should be topical DMSO applied to her head daily either by her husband or by one of the nurses at the facility.
One month after the start of treatment, there were positive signs in the lady. Her brain was starting to respond to the DMSO. The treatment continued, and four months after treatment started this lady was able to return to her home. After her return to her home, this patient started drinking one teaspoonful of DMSO in a small glass of water each day in addition to the daily topical treatment. This treatment continued for a period of years.
Three years after the start of DMSO treatment this writer returned to visit this patient. At this time the lady was living a normal life, not the life of a stroke victim. She was able to look after the house and walked normally.
The only lingering effect of the stroke was a slight speech defect. At this time she said that her memory was better than that of her husband who had not had a stroke and who was considered to be completely normal.
Note: there are also many reported cases of individuals who took DMSO for musculoskeletal or pain disorders (by far the most common use of DMSO) who then experienced a permanent improvement of stroke symptoms.
As shown earlier in this article, DMSO has numerous properties that make it uniquely suited to protect from the damage of ischemic strokes. These benefits have in turn been shown to occur for brain tissue. For example:
•In anesthetized cats, DMSO significantly enhanced brain oxygenation (particularly in the caudate nucleus).
•DMSO was shown to preserve the neurological function of hippocampal brain tissue samples once their oxygen or glucose were withdrawn (with similar results seen in this study).
•Frequently in strokes, an area will form where blood has been impaired, but brain tissue has not yet died (known as the penumbra—and the key target of most stroke management). In a pivotal rat stroke study where DMSO was administered an hour after brain blood flow had been permanently cut off, MRI imaging showed that DMSO stopped the region of dying brain tissue from continuing to expand, hence allowing a penumbra (rather than additional dead tissue) to form around the stroke site (particularly within the cortex).
Note: beyond the classic penumbra, groups of cells can also enter a shocked state where their normal functions cease (and they eventually die). As discussed here, this “penumbra” also responds to DMSO (which is one reason tissue often comes back to life following DMSO treatment).
Many animal studies have found that if blood flow is cut off to the brain, typically by occluding (blocking off) either the MCA (a key artery in the brain frequently affected in debilitating strokes) or the carotid artery, DMSO significantly reduced the resulting ischemic damage (along with the reperfusion damage resulting from the blood re-entering the ischemic brain tissue).
Note: these results argue that giving IV DMSO beforehand could reduce the complications of many challenging surgeries (e.g., a coronary bypass). Unfortunately, much in the same way ultraviolet blood irradiation dramatically reduces bad surgical outcomes, neither has been adopted for this purpose.
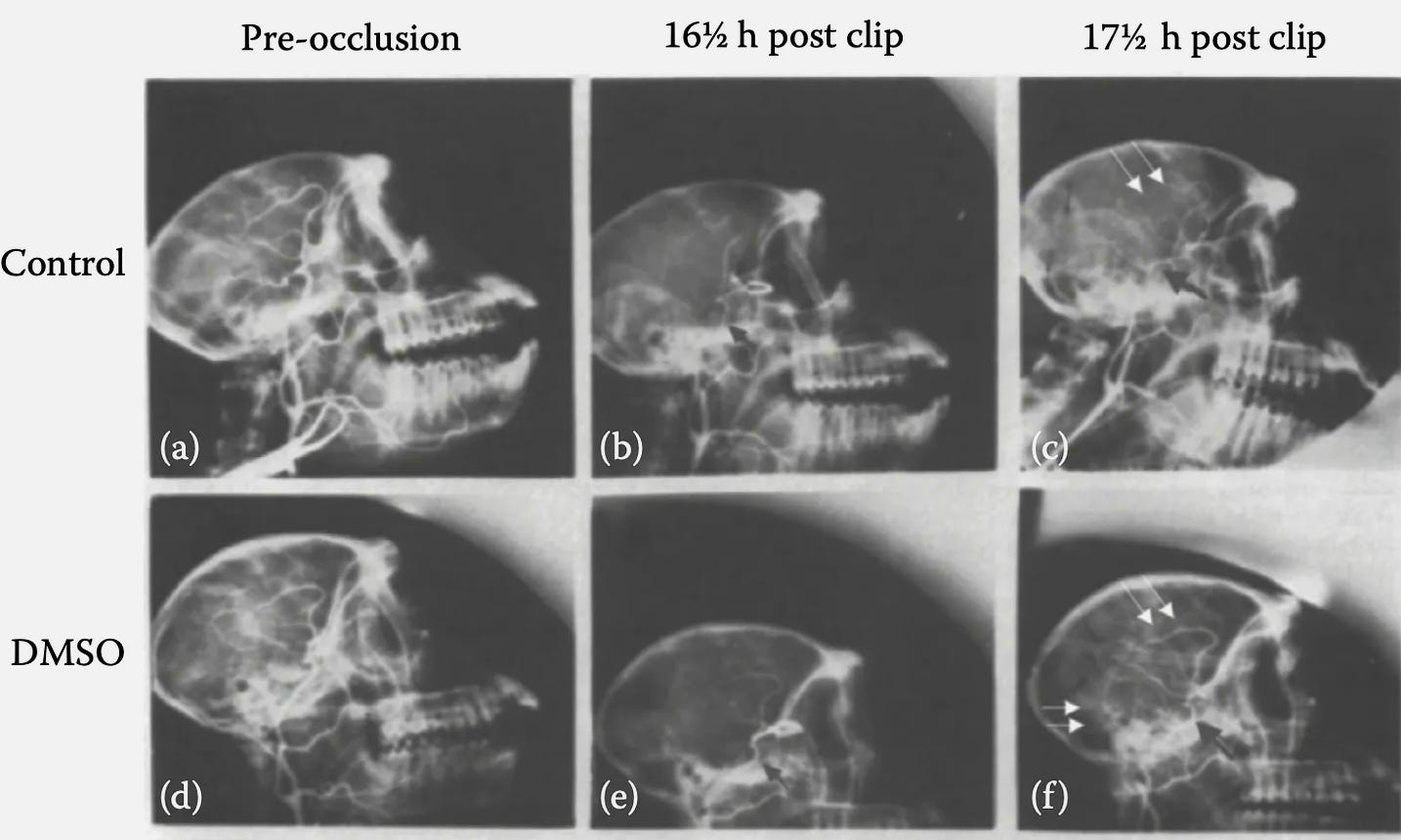
For example, a rhesus monkey study blocked the MCA for 4 hours, gave DMSO, dexamethasone, or nothing, and then opened the MCA after it had been blocked for 17 hours. DMSO gave significant protection from the severe neurological deficits and loss of arterial blood flow the other two groups developed.
A squirrel monkey study blocked the left MCA for 4 hours, and then given a variety of different treatments (e.g., saline, hemodilution, or hyperbaric oxygen at 2 atmospheres). Seven days after treatment, 8 of 10 DMSO treated monkeys were alive (with 2 having mild contralateral muscle weakness), while 75% of those receiving hyperbaric survived, and just 34% of those receiving hemodilution survived (with the last two groups also having more significant neurological deficits). Finally, combining either of these treatments with DMSO produced slightly worse results than just DMSO alone.
Similar results have also been seen in many other species. For example, in rats who experienced strokes:
•DMSO 30 minutes prior to MCA occlusion significantly reduced the amount of permanently damaged brain tissue.1,2,3
•DMSO 20 hours prior to MCA occlusion reduced infarct size by 65%, by 44% when given an hour after (or by 31% if a lower dose was given), and by 17% when given two hours afterwards. Additionally, all treated rats survived (whereas 50% of controls died), and when survivors were examined 3 days after the stroke, the infarct was significant reduced.
•DMSO immediately after occluded MCA blood flow was restored reduced infarct size (the region of lost brain tissue) and blood-brain barrier damage (as measured by MRI). When combined with DPI, this protection was enhanced and the activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 (enzymes which break down brain tissue) was reduced. Similar results were found in this study.
•DMSO preserved neuronal loss and reduced astrocytic hyper-reactivity in the somatosensory cortex and hippocampal from MCA occlusion.1,2
•DMSO one hour before or after MCA and carotid occlusion significantly reduced brain edema and infarct volume.
•DMSO 30 minutes prior to 90 minutes of MCA occlusion significantly reduced cortical and striatal infarct volumes and significantly improved neurological motor function (assessed 24 hours after occlusion). Additionally, no benefit was seen when a low dose of DMSO was used.
•Oral DMSO along with vitamins C and E, 12 hours after MCA occlusion, significantly reduced oxidative stress.
Note: in neonatal (7 day old) rats with hypoxia-ischemia (HI) brain damage, DMSO injected into the brain reduced infarct volume and brain injury (particularly within the cortex) along with inhibiting the breakdown of MAP2 and fodrin, suggesting neuroprotection via calpain inhibition.
Likewise in other animals:
•A gerbil study (this species is more susceptible to strokes) found blocking carotid blood flow to the brain and then restoring blood flow to the brain caused significantly less neuronal loss if DMSO was given 30 minutes before the carotid blood supply was cut off. Another gerbil study had similar results, another did as well, another did as well (which found the best results, such as reduced death, neuron damage, and retained motor function) were obtained with lower DMSO doses), as did a fourth (which specifically found DMSO protected against hippocampal pyramidal cell loss).
Note: DMSO was less protective in Gerbils than other species.
•Another gerbil study found DMSO given 30 minutes prior to permanent occlusion of a carotid greatly reduced seven day mortality (60% in untreated animals vs. 33.4% with low dose DMSO and 14.3% with high dose DMSO), greatly reduced neurological symptoms (e.g., drooping eyelids, hemiparesis, walking circularly only in direction) and reducing damaged brain cells by 15.6 to 35%.
•A dog study cut off cerebral blood flow, then restored it and used a variety of biochemical measurements to monitor cellular metabolism (along with EEGs). Dogs who received DMSO (and an anti-platelet agent) had significantly higher mitochondrial function (which was almost identical to controls who had not suffered the occlusion).
Another dog study induced a stroke by introducing an embolus (clot) into the MCA and then giving DMSO. Compared to controls, those given DMSO were observed to have normal behavior and no neurological deficits afterward, whereas 3 of the 9 controls died (with significant tissue death in the brain), while the survivors had contralateral paralysis (a typical stroke consequence) and impaired consciousness.
Note: another dog study found IV DMSO shunted blood to the brain, increasing total cerebral blood flow by over 20%, with increased flow to the caudate nuclei and cerebral hemispheres along with increasing intravascular volume, lowering hematocrit, increasing cardiac index with enhanced ventricular blood flow and having the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen remain stable.
A cat study found DMSO protected brain tissue from MCA occlusion and increased cerebral blood flow (CBF) by 27%. When DMSO was given in conjunction with PGI2, a greater improvement was seen (e.g., a 68% increase in CBF).
In another cat MCA occlusion study, IV DMSO reduced mortality by 75% (almost all cats survived), likely due to DMSO greatly reducing the severe postischemic vasogenic brain edema (which created life-threatening midline shifts in the brain). This study built upon a similar dissertation by one of the investigators.
In rabbits where the MCA brain blood flow was cut off for 4 hours, administering appropriate doses of 20% IV DMSO when blood flow was restored greatly reduced the resulting neuronal damage, reactive gliosis and multifocal spongiosis throughout the areas supplied by the MCA, along with reducing meningeal edema, erythrocyte extravasation, neurophil hemorrhage.
Additionally, a rat study found that when hemorrhagic shock was induced (causing a loss of blood flow to the brain), DMSO downregulated the inflammatory response (NF-kappaB) and upregulated a key protein cells use for survival (HSP70).
Note: in the studies, I reviewed, I came across two (a cat study and a gerbil study( where blood flow was cut off to the brain did not observe a benefit from DMSO.1,2
Hemorrhagic Strokes and Traumatic Brain Injuries
While ischemic strokes are difficult to treat, hemorrhagic ones (and other traumatic brain injuries) are even more challenging, and after decades, there has been surprisingly little progress in neurologic intensive care, particularly in preventing long-term paralysis and disability.
Note: conflicting evidence exists supporting the use of progesterone, hypothermia, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy for traumatic brain injuries, but none of these approaches are in widespread use. Strong evidence also supports the use of methylene blue but it also is rarely used. Finally, certain trials (e.g., with progesterone or with an adenosine kinase inhibitor) find those therapies work even better if combined with DMSO.
It was, as if the hand of God had somehow touched the [experimental] animal’s forehead. ‘I don’t believe it’, I stammered. But it was true. I felt a tingling in my spine because this reawakening of a virtually dead animal had all the markings of a medical breakthrough [Jack de la Torre MD].
Instead, the discovery, the potential for saving lives and the continued research that should have uncovered other uses for dimethyl sulfoxide and similar agents was quietly laid to rest in the coffers of forgotten medicine.
Note: Torre’s observations were partly based on the fact he saw numerous animals with flatlined EEGs (which typically precede brain death and then actual death) have the EEGs come back within 10 minutes of receiving DMSO.
When treating severe brain bleeds, a few major challenges exist.
First, swelling and the leaking of blood into the brain can dramatically increase the pressure on the brain (known as intracranial pressure or ICP). The brain’s tissue in turn is very sensitive to increased ICP or masses (e.g., a large blood clot) compressing it. Unfortunately, there is no good agent for reducing ICP (e.g., the most commonly used agents like mannitol can create a “rebound ICP” which is higher than it was at the start).
Note: there can also often be a breakdown of the blood brain barrier which causes even more fluid to enter the brain.
Additionally, inflammatory processes begin once the blood enters the brain which injures brain tissue (and triggers cell death), while simultaneously, the iron released by dying blood cells generates free radicals which then destroy brain cells.
Remarkably DMSO addresses each of these issues. For example, it rapidly lowers ICP (without the risk of a rebound) and unlike many other ICP lowering agents, does not cut the blood supply to the brain (rather it increases cerebral perfusion without increasing blood pressure or heart rate—which is important because brain cells rapidly die without a sufficient blood supply to maintain their metabolism). Likewise, improved cerebral blood flow is necessary to remove the blood that leaked into the brain (with DMSO in turn being excellent for reducing brain edema).
Note: I suspect rebound ICP is the brain’s attempt to get enough blood, and since DMSO ensures this, that’s why it doesn’t cause rebound ICP. Likewise, a study on anesthetized cats found IV DMSO (ranging from 0.0000007813% to 31.252%) never contracted the middle cerebral arteries, but at concentrations above 0.7813%, it relaxed pre-contracted arteries, and when 1% was applied to pia arterioles, it expanded them. Given then and that IV DMSO causes brain shrinkage (by removes excess fluid) without altering cerebrovascular responses to potassium ion changes, this suggests DMSO’s ability to lower intercranial pressure stems from osmotic effects rather than direct vascular actions.
Furthermore, DMSO lowers many of the inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1α, IL-1β, and IL-6) associated with strokes and tissue injury (along with macrophage chemoattractant protein-1) and inhibits capping of surface receptors including those in lymphocytes (which calms an overactive inflammatory response).
Finally, a study showed that DMSO’s inhibition of platelet aggregation at injured microvessels and inhibition of dilation of injured pial arterioles (near the brain) is likely due to its scavenging of free radicals, explaining its brain injury–specific effects—such as preventing blood from flooding the injury site and reducing the risk of secondary ischemic injury.
In short, as far as I know, no comparable agent exists for lowering ICP (one of the greatest challenges in neurocritical care), and in turn, many (unsuccessful) agents have been tried (in part because what works in animals often does translate to human brains).
Furthermore, beyond directly removing edema (water) from the brain and bringing it back to the bloodstream (which is how it lowers ICP), limited experiments done in humans show DMSO is somehow able to reduce the spilling of blood into the brain (the mechanisms of which has not been worked out).
Additionally, DMSO also addresses many other critical aspects of traumatic brain injuries and brain bleeds (which under conventional care requires many different drugs):
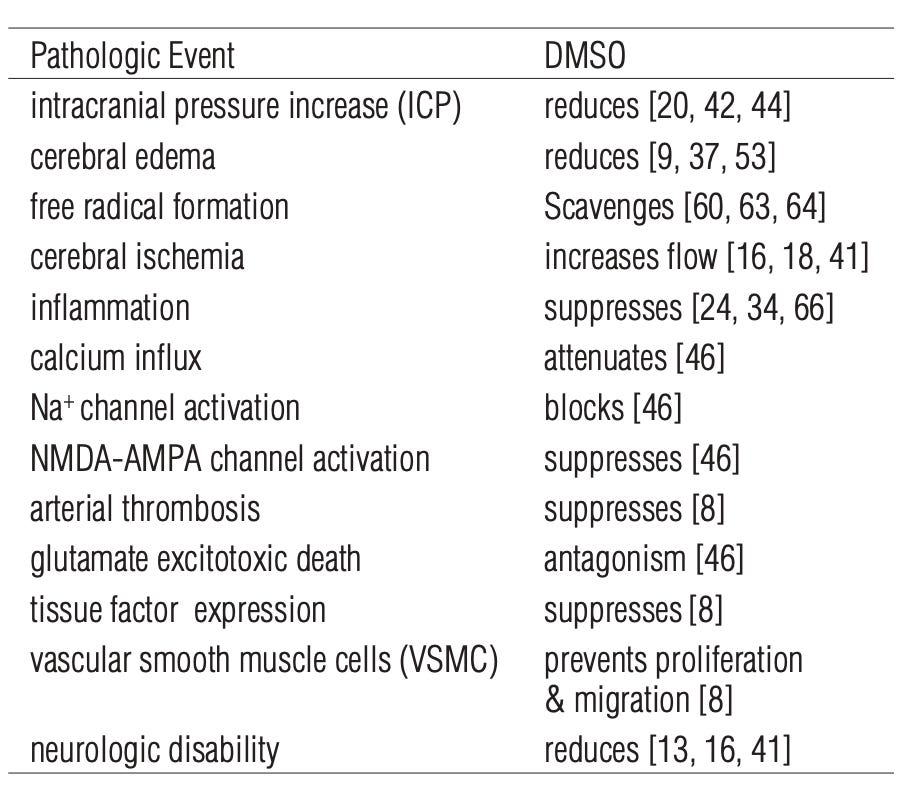
Note: DMSO also lowers the JAK2/Stat pathway, suppresses neurotoxic NMDA-AMPA-induced ion currents, prevents iron induced lipid peroxidation and focal edema, and as mentioned above, protects cell membranes.
A variety of studies have been conducted that demonstrate DMSO’s remarkable therapeutic potential in these situations.
Brain Bleeds
•In experimental brain hemorrhages when intraperitoneal DMSO administered one hour after the bleed, in rats it prevented increases in brain conjugated dienes and fluorescent products (maintaining antiradical activity) while in cats, it improved cerebral hemodynamics, preserved oxygen and glucose metabolism near baseline levels, and greatly reduced mortality (0% vs. 25% in controls by 3 hours).1,2
•A study examined 11 adult patients with high ICP and a GCS score of 4–6 following brain trauma or subarachnoid hemorrhage (standard therapy did not work) who were on the verge of dying. DMSO was then given, which immediately reduced the ICP (and induced diuresis), with 3 (who had been expected to die) then surviving.
Note: it was also concluded this study demonstrated the value in keeping the cerebral perfusion pressure above 60mmHg (something DMSO helps with) even in the presence of high ICP.
•One paper reported on nine patients who suffered a partial or total hemiplegia (paralysis) after surgical repair of an aneurysm:
In a 61 year old male (R. MCA and R. carotid), DMSO was initiated after surgery due to blood pressure climbing and left-sided paralysis developing, and in 30 minutes, blood flow increased in the right brain region by 20% (and 11% on the left), the patient’s condition greatly improved. DMSO was then stopped day 5, and paralysis (and confusion) rapidly came back, after which DMSO was resumed and the patient fully recovered.
A 67-year-old woman (L. MCA) lost the ability to speak and developed right-sided paralysis after surgery. After 8 hours DMSO was started (as mannitol didn’t work), and within 45 minutes she became fully alert and regained her strength, within 2 hours her cerebral blood flow improved, and within 12 hours her motor strength permanently normalized.
A 25-year-old woman was hospitalized with severe headache and high blood pressure from a L. MCA aneurysm (and spasm in the internal carotid). 12 days after surgery, she suddenly developed right-sided weakness, right-leg paralysis, and difficulty speaking. After 8 hours of mannitol didn’t help, DMSO was started, and within 90 minutes she could lift her leg, and by the following day she had fully recovered.
A 28-year-old woman developed excruciating headache and right sided weakness from an MCA aneurysm who then developed a severe internal carotid spasm that did not respond to standard care but did from DMSO (allowing her to have a completely recovery).
The remaining five cases of a hemorrhaging aneurysm had a similar course to the above cases after rapidly responding to DMSO, with all but one patient (who had a variety of severe exacerbating factors) making a full recovery. Additionally, no adverse events were observed in any cases.
Likewise, this is a story I from a South African reader:
I saw your post on DMSO, bought a bottle, and three weeks later, I had a (nonaneurysmal) brain hemorrhage after an ice bath. My partner immediately applied DMSO and then I went to the hospital, then went home an resumed topical DMSO. Your research, information and help allowed me to trust and use the DMSO [I spoke to her after the initial]. After three weeks, I had a followup scan. The neurosurgeon who looked at the scan said he was surprised that I did not get cerebritis after the hemhorrage and was also surprised that I had such a marked improvement after such a short time. I’m sending you my MRI scans (11 days apart) for evidence of the effectiveness of DMSO in the hope this will help someone else. Thank you DOC!!!!
Note: another reader’s partner (aged 75) was suddenly diagnosed with an inoperable 8cm glioblastoma causing a slow brain bleed, losing the ability to speak, and right-side paralysis, with a prognosis of 3 weeks to live. After copious topical 99% DMSO motor function began returning within 24 hours and over the next week, the partner regained the ability to feed himself, communicate using Google Translate, and perform basic activities. By week 3, he was eating meals at the table, and by week 4, he could walk with a walker and engage in cognitive activities. A new CT scan at day 55 showed no brain bleed and reduced tumor metrics (a longer summary can be found here).
Severe Head Trauma
•In ten patients with severe closed head injuries found DMSO rapidly reduced ICP, increased cerebral perfusion without affecting the systemic blood pressure and patient responsiveness (except in one patient), and most importantly improved the neurological course and outcome of the illness.
•In a follow-up study, ten patients with closed head trauma and elevated ICP (40-127 mmHg compared to the normal 5-13 mm Hg) received IV DMSO, with an ICP drop in most cases happening within 30 minutes, and averaging 28mmHg after 24 hours, and 58mmHg after six days. Most patients then took 2-10 days to have the fluctuations in their ICP diminish. The reduction in brain swelling following DMSO treatment was confirmed by CT scans. All patients had a neurological assessment six days after the DMSO treatment. Six patients had mild or no problems, two had moderate impairment, and two had severe impairment (two patients eventually died of their injuries). Three months later, seven patients had minimal to no impairment, while one patient showed no improvement. No adverse effects from DMSO were observed.1,2
•In 12 patients with traumatic brain injury and elevated ICP, IV DMSO (on average given twice) rapidly reduced ICP 91% of the time (with the non-responding cases not responding to standard agents either). No side effects or other adverse changes (e.g., reduced brain perfusion) were noted.1,2,3
•A trial of 35 patients with severe head injury undergoing emergency cranial surgery found IV DMSO controlled ICP in 75% of cases, whereas standard therapy did so 53% of the time and in those that did not respond to conventional therapy, subsequent DMSO controlled ICP in 50% of them.
•At a 1980 Congressional hearing on DMSO, Dr. Stanley Jacob discussed data presented at his medical school on 11 patients with severe head injuries and markedly elevated ICP, 6 of whom did not respond to other ICP treatments, but within 3-5 minutes all had their ICP come down to normal, along with similar 5 patients who were started on DMSO and ultimately had a much better outcome than those where DMSO was started later.
Finally a report discussed by Dr. de la Torre (which I could not locate), detailed five patients with closed head injuries and a high ICP which rapidly lowered from IV DMSO. A 1.5 year old with a GCS of 7 and ICP of 30mmHg fully recovered over 3 weeks, while a 7-year old child admitted with a GCS of 5 and an ICP of 25 mmHg fully recovered after 8 weeks at the hospital. The three other patients (aged 17-52 with GCS scores of 3-5 and two having ICPs above 50 mmHg) initially responded to DMSO but did not survive.
Animal Brain Injury Research
The above results have also been demonstrated in a variety of animal brain injury models:
•In rats with fluid percussion induced TBIs, DMSO reduced the number of degenerating and dying neurons.
•A rabbit study created lethal brain edema (and increased ICP) by freezing part of the brain. DMSO was observed to significantly reduce ICP and brain edema after 5 minutes while increasing cerebral perfusion and not changing central venous pressure. This was then followed up with a study that had similar result, another study with similar results that used a slow infusion rather than a bolus, with a study that achieved similar results with a different DMSO dose, two more studies with similar results1,2 (where a synergistic effect was seen when used with a barbiturate as the ICP reduction was enhanced but the barbiturate reduction of brain blood flow was counteracted), another similar study which found these effects were likely mediated through sodium mobilization, and a final set of studies with similar results that also showed indomethacin partly blocked DMSO’s reduction of ICP, suggesting it is partly mediated by prostaglandins.1,2,3 Additionally, this Chinese study also used DMSO to treat acute cerebral edema.
•In rabbits with brain edema induced by injecting a pertussis vaccine directly into the carotid artery, IV DMSO effectively reduced ICP and brain edema.
Note: the older pertussis vaccine (which was notorious for causing severe brain injuries) contained a toxin which disrupted the blood brain barrier and created brain inflammation. In this study, that (alongside injecting it to the artery that feeds the brain) was used as a reliable way to induce brain damage.
•In rats with brain edema induced by injecting FeCl₂ (iron) into to the brain, concurrently administering intraperitoneal DMSO initially reduced brain edema by 23.20%, and after 24 hours, DMSO treated rats had 73.95% edema than untreated controls.
Pressure Injuries
Anytime there is a brain bleed or concussive impact, a risk always exists that pressure will be put on part of the brain (e.g., from an expanding clot). DMSO has been repeatedly been shown to mitigate this dangerous situation:
•An expanding balloon (designed to stimulate a hematoma) was placed in the brains of 40 monkeys, 15 of whom received DMSO. Of the DMSO treated monkeys, 1 (7%) died, and 1 developed mild right side paralysis. In contrast, 90% of those who received saline died (with the survivor having severe neurological deficits and dying the next day).1,2
Note: This study was preceded by an earlier study of 30 monkeys with similar results.
•In dogs with reduced blood pressure, pressure was applied for an hour directly to the brain, cutting off cerebral blood flow and creating, brain necrosis, cavitations and edema at the site of pressure, along with neurological deficits on the opposite side of the body (controlled by that part of the brain). Compared to variety of agents (e.g., barbiturates, mannitol, dextran, methylprednisolone), DMSO was the most effective in reducing the resulting brain damage. Compared to no treatment, DMSO improved neurobehavioral scores by 220%, reduced brain lesion volume by 93%, greatly reduced histological damage in the brain, and prevented almost all of the dogs (5 out of 6) from dying. Additionally, since alcohol in the bloodstream increases the damage from a traumatic brain injury (which happens during drunk driving), this experiment was repeated with high blood alcohol levels, where DMSO was then found to reduce the resulting brain tissue damage by 60%.1,2
•Pressure-induced ischemia was applied directly to the somatosensory cortex of dogs, resulting in half dying within 12 hours and the rest dying 3-5 days later. When IV DMSO was given beforehand and after every 12 hours for three days, only one out of six dogs died, while the five survivors showed no neurological or behavioral changes (although histological changes in the brain were present). Additionally, somatosensory evoked potentials were preserved in the treated dogs which survived (whereas they disappeared in the untreated dogs).
Note: one of the interesting findings in a few animal DMSO brain injury studies was that neurological function was preserved despite injury being present in the brain tissue.
Lastly, another study which evaluated seven different therapies found DMSO was the most effective in attenuating neurobehavioral signs and histological responses to pressure-induced focal ischemia.
Impact Studies
Numerous studies have attempted to simulate closed head trauma by dropping weights on the heads of animals:
•In injured rats, DMSO was found to reduce neuronal apoptosis (death).
•In rats, DMSO significantly increased Bcl-2 gene expression compared to controls, reducing cell death across 6 to 168 hours post-injury.
•In rats, DMSO significantly improved cognitive and locomotor function (e.g., solving mazes) while reducing anxiety compared to untreated TBI rats. Additionally, DMSO reduced oxidative stress, inflammation, necrosis, and axonal damage was reduced in the brain tissue.
In rats, oral DMSO following brain injury reduced memory deficits observed a week later by 62%.
•In rats, DMSO increased Survivin and NF-κB expression in injured brain tissue at 1, 2, 3, and 5 days post-injury compared to controls, reducing cell apoptosis.
•In mice, post-injury fructose 1,6-diphosphate (FDP) and DMSO synergistically combined to prevent brain injury, demonstrated by significant motor function protection (via the grip test), significantly higher survival rates, and histopathological analysis showing a marked protection of cortical and hippocampal CA1 neurons.
Note: in animal experiments simulating severe brain injury, DMSO has also been shown to strengthen their respiration (whereas in many cases it instead becomes shallow and may eventually stop). Additionally, in both humans and animals, DMSO (due it functioning as a diuretic) will often significantly increase urination.
Missile Injuries
To simulate DMSO’s protective effects against gunshots, missile injuries (frequently with BB pellets) were created in monkeys. Compared to mannitol, DMSO was found to create significantly better cerebral perfusion and oxidative metabolism along with achieving an 86% survival rate (vs. 75% survival for mannitol and 55% for the untreated group). Those were results were replicated in a more detailed followup study, and two other studies by different researchers.1,2
To put all of this into context:
A January 11, 1981, a news report in the Ocala Star Banner [page 6], carried the headline: “DOCTOR CLAIMS DMSO SAVED 11.” The story read:
SAN DIEGO (AP)—A doctor at the University of San Diego credits the controversial drug DMSO with saving the lives of 11 people who suffered severe head injuries.
Dr. Perry E. Camp, a UCSD Medical School neurosurgeon, said Friday that dimethyl sulfoxide was effective for 11 of 30 people judged near death and for which other lifesaving methods have proved useless.
“To take patients like that and have even one out of 10 survive is phenomenal,” Camp said. “The fact that we have any survivorship at all . . . doesn’t sound like much, but it is extremely encouraging,” Camp said.
Sadly, however, despite the immense amount of research conducted and these results being dramatically better than what the standard of care can offer, this remains an almost completely forgotten side of medicine. That said, one treatment for brain arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), Onyx, is composed of a polymer dissolved in DMSO, which solidifies into a cast to occlude abnormal vessels, reducing blood flow and the risk of future hemorrhage and often is used as a presurgical measure.
Note: other DMSO polymor mixtures are also used (e.g., in this study of 16 patients who received a newer one, there was an average AVM size reduction of 85% with 62.5% having the AVM completely cut off, and no complications being experienced by any of the participants.
Concussions
Many of the same principles hold true for concussions, and the pioneers of DMSO felt it was an essential treatment for athletes after they experienced one—particularly since concussions can predispose the athlete to long-term cognitive issues (e.g., both boxers and professional football players have a threefold risk of dementia).
In addition to the previously highlighted animal studies showing DMSO protects the brain from traumatic impacts consider this one, where, in rats with diffuse axonal brain injury, DMSO significantly reduced c-fos and c-jun gene expression in neurons across the cortex, white matter, brain stem, thalamus, and cerebellum, with the most pronounced reduction observed 2 hours post-injury compared to controls. These genes drive inflammation and neuronal cell death after traumatic brain injury, so DMSO’s ability to suppress their expression during the critical early window for mitigating concussion-related complications highlights its substantial therapeutic potential.
Likewise, there are also periodic cases of dramatic concussion recoveries following DMSO. For example, one author shared the case of a woman who had received a severe concussion from falling off a horse, after which she had trouble walking, would suddenly neurological decompensate (e.g., she would drop something), and had memory issues alongside foggy headaches. Thirteen years later, she received an injection of DMSO, immediately had a large improvement, and further improved with subsequent injections.
Note: the most detailed paper summarizing DMSO’s protective effects from brain and spinal cord injuries can be read here.
Spinal Cord Injuries
We used to think that the damage caused at the moment of injury in a severe head or spinal cord injury was irreversible. But now there are animal studies and a handful of clinical cases that tell us something different. There is still a little bit of time before the injured cells die. Based on what we’ve seen in animal studies and a handful of human situations, we think that if you can treat a head injury victim within a few hours of the injury, or a spinal cord victim within one hour, there is a good chance of preventing death or the paralysis that would otherwise occur.—Dr. Jack de la Torre“
We have had three patients come into our medical center paralyzed after injury: one five hours, a second six hours, and the last nine hours. Historically, we thought their chances of recovery were just about zero. Two of those three are now walking as a result of our administering IV DMSO despite the time being beyond an hour-and-a-half of the injury.—Stanley Jacob MD
Note: one of DMSO’s unique properties is that it can induce stem cells to differentiate into cells needed in specific parts of the body (e.g., I detailed the data it does so for many organs such as heart here). As such, when DMSO was combined with brain derived neurotrophic factor (which concentrates in the central nervous system), it caused rat bone marrow stem cells to differentiate into neuron-like cells which can regenerate damaged nervous tissue.
Since central nervous tissue does not regenerate, classically, strokes and spinal cord injuries are considered to be incurable (e.g., despite decades of research, the standard of care is still using steroids—despite the existing evidence showing they don’t work and them having many side effects).
Note: one survey found that the primary reasons spinal surgeons use steroids for spinal cord trauma is to avoid being sued.
As much of the same pathology that causes permanent damage in the brain also occurs in the spinal cord (the loss of blood flow and compressive post-traumatic swelling), DMSO can produce miraculous results. In turn, when the pioneer of medical DMSO, Stanley Jacob MD, was asked who would benefit the most from DMSO being adopted by medicine, his response was immediate:
'As I get to know the quadriplegics, ever so many of them eventually will say to me, 'You know, Dr. Jacob, I couldn't even commit suicide.'
In turn, like strokes, the greatest benefit from DMSO is seen if it is given (intravenously) within 90 minutes of the injury (e.g., de la Torre found that giving DMSO to dogs shortly after a spinal cord injury that typically produced permanent paralysis were spared from it and regained almost normal function within a few weeks). Likewise, the sooner to an injury, the more dramatic the improvement is:
At this time, Jacob was treating eight quadriplegics; and of them only one had presented a recently incurred injury. He felt, as do most doctors, that treatment is more fruitful in new than old conditions. The one fresh case was that of a sixteen-year-old girl, a fine athlete, who dove off a board and landed on her neck on the bottom of the pool.
Her doctor was pessimistic but willing to try almost anything that offered a glimmer of hope. She was a complete quadriplegic—utterly helpless.
She was on DMSO for an entire year. Gradually—one by one, it seemed—her organs began to function again. Eventually she walked. And now she is in college, doing very well.
However, at the same time, DMSO can often provide significant rehabilitation for far older injuries.
An Orange County, California, engineer suffered a severe back injury in an automobile accident. He was paralyzed below the point of injury and was confined to a wheelchair. However, his spinal cord was not severed. It did suffer damage, but there was no break. DMSO treatment was offered, but this man refused the treatment. He was convinced that it would not work, and he would never walk because a few months after the accident he still had no feeling in his legs.
Twelve years after the accident this man changed his mind and decided to try topical treatment with a DMSO lotion. The lotion was applied twice a day to the entire back of this patient. After three months this man was able to move the toes on his right foot. He never regained the ability to walk, but the treatment restored some feeling and the ability to move a part of his body below the injury site.
Our son had been in a coma due to an auto accident. After six months in the hospital we brought him home. His Drs. said that he would probably never regain bladder control. In 1973 he became a patient of Dr. Jacob. Within months of using DMSO he had full bladder control.
“We have had experience at our medical school in Oregon with two patients in which DMSO was given as early as an hour after what was considered an irreversible injury—an immediate, complete quadriplegia—and in both people there was total recovery with them walking out of the hospital,” said Dr. Jacob.
The neurosurgeon told me [his mother] that henceforth Grey's only motion would be to move his head from side to side and grin [due to a C4-C5 fracture that had blocked the cord there]…Grey listened attentively and thought a minute; then said to the doctor, "One day I will swing my legs off my bed and I will offer to bet you I am going to walk. At that time, put your money where your mouth is now.
In insisting that her son would find help, Dorothy Keinsley did not delight all the doctors. "One doctor bellowed at me like a bull moose in rutting season," she said. "Don't you know your son is paralyzed?" He screamed. I explained that no one knew it as well as I."
Grey read Ann Sullivan's article about DMSO…He wrote to Jacob, and his physician made the tests Jacob had required. On February 13, 1965, Jacob came to [Gray’s] Littleton [CO] home free of charge and swabbed Grey's neck with DMSO.
'The most dramatic change happened that first day," Dorothy told me. "Grey had had a constant pain in his right shoulder from the time of the accident, and he had learned to live with it. Late that day, Grey discovered the pain had gone. He was almost incredulous. He expected the pain to return, but it never has."Other improvements were gradual, as Dr. Jacob had predicted they would be.”
Note: Gray made remarkable improvements which eventually stopped (but did not regress) due to the FDA unconscionably revoking the medical use of DMSO.
As far as I know, while many compelling cases (e.g., those just mentioned) exist, unlike strokes and severe blunt head traumas, no formal studies on DMSO after spinal injuries have been conducted in humans. However, as shown previously, mechanistically there is evidence to support that use (e.g., this study showed that DMSO prevented the degenerative changes in spinal cord nerves after blunt trauma), and a variety of corroborating animal studies, all of which led the leading researcher in this field to conclude that if a severe spinal cord trauma is treated with intravenous DMSO within 2 hours, paralysis may be prevented.
Note: animal studies also showed the greatest benefit from DMSO occurred if it was given within 2 minutes, and that higher DMSO doses also increased the speed and likelihood of recovery.
Many studies in turn have simulated the spinal cord injuries (typically by exposing the cord and then applying a precise blow to it), after which the recovery of DMSO treated animals is compared to untreated animals and placebo.
The results are often quite remarkable. This for example came from De La Torre’s research:1,2,3
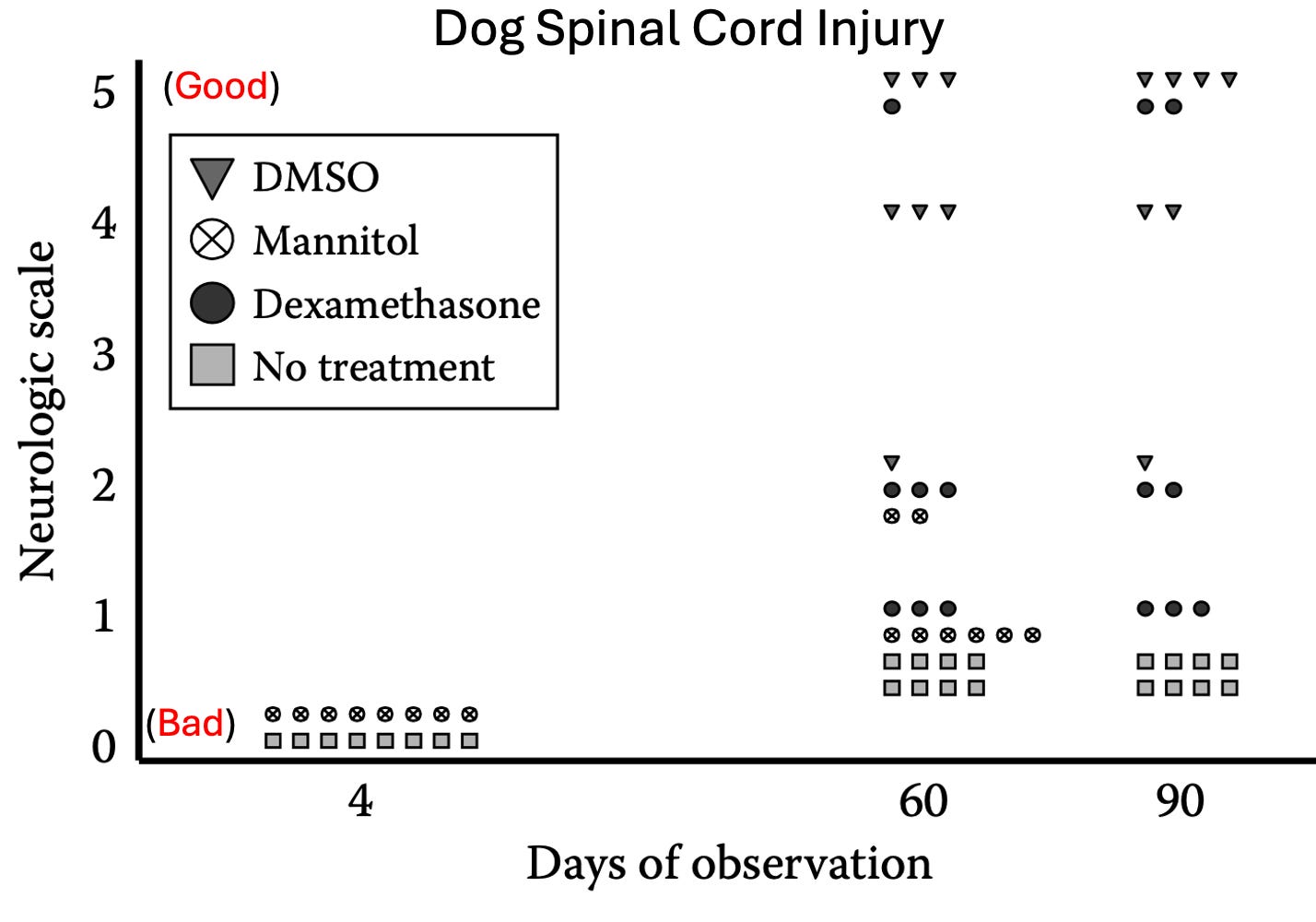
These results have been corroborated by other blunt trauma spinal cord injury studies:
•In rabbits, DMSO significantly accelerated recovery of hind leg motor function, normal urination and defecation, and repair of the laminectomy site with new skeletal tissue (whereas untreated rabbits showed no motor recovery). Additionally, the spinal cords of DMSO injured rabbits had 14% less edema, healthier neurons with vigorous metabolism, nuclear cleavage, and more normal cells.
•In cats, DMSO was shown to improve functional recovery from spinal cord injuries by 169.57%.1,2,3
•When a spinal cord injury occurs, one (still largely experimental) treatment is to attach part of the highly vascularized omentum to it. In cats, IV DMSO was shown to significantly extend the amount of time that could be waited before doing this (6-8 hours instead of 3) and to work much better there than any other existing therapy (e.g., methylprednisone).
•In rats, compared to controls, DMSO treatment reduced free radical content (MDA) and increased antioxidant activity (SOD) after 96 hours, improved hindlimb motor function by 24–96 hours, and lessened neural tissue damage.
•In rats paralyzed by a traumatic spinal cord injury, within 5 days, DMSO significantly improved motor function although no corresponding histological changes could be observed within the spine.1,2
•In rats, DMSO given following a therapy was found to significantly improve the motor function and somatosensory-evoked potentials of the hind legs (compared to methylprednisone or naloxone).
Note: numerous studies have found DMSO improved somatosensory-evoked potentials and that their presence correlates with an improved prognosis and an eventual full recovery.
•In dogs, IV DMSO and spinal surgery resulted in the recovery of walking, running ability, cortical-evoked potentials, and histological improvements (less cavitation, meningeal hyperplasia, and necrosis of the cord), whereas dexamethasone (a steroid), reserpine and hypertonic dextrose did not offer any improvements.
In dogs with injuries that caused permanent paraplegia in all 9 untreated controls, over 6 weeks, 6 DMSO treated dogs fully recovered, 2 showed improvement, and had no response to DMSO.
Likewise, other types of spinal cord trauma have also been studied.
•In two different rat studies, when the spinal cord was cut, DMSO following the injury was found to be superior to both hyperbaric oxygen and placebo in allowing the rats to avoid being paralyzed and in reducing the subsequent damage to the spinal cord (e.g., less scarring, collagen formation and damaged nerve fibers).1,2. Likewise, a third found DMSO prevented a variety of pathological changes in the spinal cord (which was hypothesized to result from DMSO removing fluid pockets commonly seen after spinal cord injuries created space for nerves to regrow).
Note: when guinea pig spinal cord nerves were cut, DMSO significantly enhanced their recovery (axolemmal resealing), with the magnitude of effect being dependent on temperature and calcium ion concentration.
•After cats had their spinal cord become gradually compressed, DMSO restored the somatosensory evoked, and half regained some of their ability to walk.
Note: in another dog study, DMSO was used to treat intervertebral disc syndrome (discs compressing the spinal cord).
•In rabbits with spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury, DMSO improved neurological function (e.g., the ability to walk), reduced neuronal damage and reduced systemic oxidative stress. Similar results were found in a much earlier study.
•When the blood supply to the spinal cord was cut off in dogs, DMSO was shown to prevent ischemic myelopathy (damage) to the spinal cord and paralysis.
Lastly, a 1983 veterinary textbook for horses highlighted that IV DMSO (0.9-1.0 gm/kg) at 30-40% once a day for 3 days (followed by once a day every other day for 3 more days) was a very helpful for brain and spinal cord injuries in horses (including when they were comatosed) and noted that other veterinarians used 1g/kg of 10% DMSO in 5% dextrose). It also noted that in horses with cervical vertebrae lesions compressing the spinal cord, veterinarians had success giving 1cc/kg of DMSO in 1 liter of saline every other day until improvement was noted.
Note: DMSO has also been shown to treat many other complications of spinal cord injuries. For example, many paraplegics suffer from retrograde ejaculation (where the semen goes backwards into the bladder), and Dr. Jacob found these patients responded to DMSO (e.g., having less bladder infection), along with other benefits such as less bedsores and better body temperature control.
Peripheral Nerve Injuries
DMSO’s neuroprotective qualities also extend to individual nerves:
•In rabbits with sciatic nerve compression (which damages the nerve), both functional tests (e.g., pain sensitivity, motor function, and electromyography) and histopathology showed topical DMSO (50%) promoted nerve regeneration.
•In rats whose sciatic nerve was cut, local or intraperitoneal DMSO also improved nerve regeneration, along with reducing perineural adhesions. Compared to untreated rats, significant improvements were seen in the following metrics: gastrocnemius muscle weight ratio (+50%),nerve growth factor expression (+227%), myelin basic protein expression (+165%), myelinated axon counts (+26%), compound motor action potential (+935%), conduction velocity (+303%), toe-spread test (+50%).1,2
•In cultured rat superior cervical ganglia, local application of 100% DMSO (10 µl) delayed axon degeneration for up to 12 hours by preserving axonal structure and slowing microtubule degradation. This protective effect was comparable to that of nerve controls overexpressing the WldS protein, a well-established standard in nerve protection research known for preventing axonal degeneration.1,2
DMSO, in turn, has been reported in numerous studies to treat peripheral nerve diseases.1,2,3 For example, in one study of 65 patients, DMSO mixed with 1% nicotinic acid applied to the affected part of the face as a compress 10-12 times and was shown to provide a statistically significant improvement in the number cured and the duration of therapy they required.
DMSO and Protein Folding
Chemical chaperones are small molecules that help proteins be folded into their correct configuration, and hence can ensure protein stability or help the body eliminate misfolded protein. Since many challenging diseases (particularly genetic ones) are a result of misfolded or non-functional proteins, chemical chaperons offer a potentially invaluable therapeutic strategy.
Note: I believe the physiologic zeta potential has an important role in ensuring the correct folding of proteins.
Some of the best-known chemical chaperones include glycerol, deuterated water, and DMSO (which is thought to be in part due to it creating a tighter packing around proteins and stabilizing their confirmation). DMSO, in turn, has shown promise in the following misfolding diseases:
•In nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (by rescuing mutant vasopressin V2 receptor proteins). Additionally, this study showed DMSO created a functional improvement of the cells.
•In cystic fibrosis by helping transport functional CTFR proteins to the cell membrane.
•In Machado-Joseph disease (a neurodegenerative disease characterized by discoordinated movement and eventually paralysis) by preventing aggregation of the ataxin protein and cell death caused by those aggregation.
•Increase the ability of impaired immune cells (due to them having defective HLA-DM) to present the antigens necessary to mount an immune response.
In Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (a horrible and terminal condition), it reverts the mutant prion protein back to normal and prevents neurons from dying. DMSO has also been shown to prevent the aggregation of the scrapie protein (a related neurodegenerative condition). Most importantly, in animals, DMSO has been shown to improve scrapie infections.
Note: since many cancer causing proteins are misfolded proteins, it is thought that this may partly explain DMSO’s anticancer properties.
Lastly, DMSO’s stabilization likely extends beyond misfolded proteins to critical cellular structures like microtubules, essential for neuronal function and impaired in neurodegenerative diseases. A study showed DMSO and glycerol stabilized brain microtubules during isolation, preventing tubulin depolymerization under stress—likely enhancing DMSO’s neuroprotective effects in brain injuries like strokes or TBIs, where microtubule collapse from oxidative stress or ischemia worsens neuronal damage.
Amyloidosis
One of the most well-known protein misfolding conditions (which sadly is has also been linked to the COVID vaccines) is amyloidosis, a challenging to treat condition where misfolded proteins are produced in excess, clump together in the body, and gradually fill up organs, increasingly disrupting their function.
DMSO appears to have the ability to both dissolve amyloid aggregates and eliminate them from the body, and in all cases where it has been attempted, no adverse effects were observed (e.g., see this study). As a result, at least 40 studies and case reports have shown that DMSO can treat numerous types of amyloidosis.1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37. 38, 39,40 Some of those studies are as follows:
•Amyloidosis was induced in mice by repeatedly injecting them with casein and then treating them with DMSO. In mice that did not receive DMSO, their livers were loaded with amyloid, whereas in the treated mice, their livers were free of amyloid deposits, and broken up amyloid fibrils were found in their urine—demonstrating that DMSO dissolves the amyloid protein. Similar results were obtained in another study which concluded DMSO caused amyloid protein fragments to be eliminated in the urine and another study that found DMSO was effective in inducing the resorption of amyloid.
A study of low leukocyte mice (who spontaneously develop amyloidosis after one year of age with amyloid deposits in the spleen, liver, and kidney) found subcutaneous DMSO, given for two to five weeks, prevented amyloid formation in eight of ten mice. Amyloid-like material was not detected in the urines of treated or control mice.
A study that found hereditary amyloidosis in the white Pekin duck was ameliorated by administration of oral DMSO.
•A human study found DMSO caused amyloid proteins to be eliminated in the urine.
•A case report discussed a dog diagnosed with hypoalbuminemia, proteinuria, and renal amyloidosis. Two years after the initiation of DMSO treatment, the 24 hour urinary protein excretion returned to normal, while serum albumin concentrations increased to within the normal range.
•A case report discusses a woman with multiple myeloma and systemic amyloidosis who took DMSO for 4 years and had her cutaneous lesions improve (she, in turn, remained in good health 4 years after diagnosis—in comparison to a median survival time of 14.7 months). In another case report, a woman with pulmonary amyloidosis (due to multiple myeloma) received transdermal DMSO for 8 weeks, and experienced a dramatic regression of her pulmonary infiltrates (shown by x-ray) and a corresponding improvement of her arterial blood gasses. Finally another case report also showed DMSO significantly benefitted pulmonary amyloidosis.
•A retrospective study evaluated 10 patients who had developed secondary amyloidosis from rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease or Adult Still's disease (that were developing gastrointestinal complications and early stage of renal dysfunction from their amyloidosis) who took 3 daily doses of oral DMSO (in juice) after meals, dosed at 3–20 g/day in a 33% solution. This improved the renal function in 5 out of 10 renal amyloidosis patients (those given it earlier in the disease process), but did not help those who already had severe or advanced renal dysfunction. In six patients, specific improvements were seen in gastrointestinal amyloidosis, and GI symptoms such as diarrhea, and protein-losing gastroenteropathy.
•In patients with amyloidosis secondary to leprosy, like the previous study, DMSO was found to improve those with moderate but not severe renal failure (whereas the prior placebo gave no improvement).
•In another study of patients with primary or secondary amyloidosis, oral DMSO improved the kidney function of those with secondary amyloidosis and the authors emphasized that DMSO may significantly improve the length of survival for patients with secondary amyloidosis. These results were also seen in another study where patients with secondary amyloidosis from rheumatoid arthritis, following 3-6 months of DMSO, had an improvement in their kidney function and a decrease in the inflammatory activity of their rheumatoid arthritis.
•Two patients with secondary amyloidosis (due to rheumatoid arthritis) with renal failure received oral DMSO, 15 g daily, for one year and had an improvement in creatinine clearance, proteinuria, SSA (amyloid A) and CRP. Another case study had similar results.
•A girl with amyloidosis secondary to juvenile rheumatoid arthritis received topical DMSO and experienced a significant improvement in her gastrointestinal symptoms, kidney function (improved creatine clearance and a large decrease in her proteinuria), and heart (the amyloidosis had caused decreased left ventricular function).
•DMSO was given to patients with familial amyloidosis [FA], and was observed to cause urinary excretion of degraded amyloid proteins, with roughly half of the patients experiencing some degree of clinical improvement. In another report, two patients with FA causing peripheral neuropathy experienced significant improvement from DMSO.
•Another study of 13 patients who developed amyloidosis from a variety of causes found secondary amyloidosis was improved with DMSO.
•A small study of patients with primary amyloidosis localized to the bladder (a challenging condition) found the majority of patients benefitted from DMSO, that DMSO can be a bladder saving measure, and that it can help resolve obstructions between the bladder and ureters. This case report and this case report, and this case report (of two patients) had similar results.
•Six patients with amyloidosis were treated with oral DMSO, with improvement noted in two.
•A study (reported at a symposium) found DMSO successfully treated human amyloidosis secondary to rheumatoid arthritis (which was also further discussed at the symposium).
Many other studies also exist in this area. For example:
Lastly, Niemann–Pick disease (a fatal and incurable condition) results from a genetic defect which causes metabolites to excessively accumulate with cells because the proteins that should remove them don’t function properly. This disease frequently leads to severe complications such as severe neurological impairment, gradual loss of cognitive function, and organ swelling. In this, this, this, this, and this study, DMSO increased the cell’s ability to remove those metabolites, and according to this paper, oral DMSO clinically improved Niemann–Pick type C patients (e.g., there was a reduction in hepatosplenomegaly and seizure frequency).
Since abnormal protein aggreggates contribute to key neurodegenerative diseases, DMSO’s ability to remove them has been a frequent focus, particularly in Alzheimer’s disease (e.g., part of an Alzheimer’s symposium focused on this use of DMSO and a computer modeling study indicated DMSO inhibits amyloid-β aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease by modulating the stability of the Lys28-Ala42 salt bridge and enhancing interactions of aromatic residues with carbon nanotubes).
Additionally:
•DMSO was found to increases the activity of lysosomal alkaline phosphatase (ALP) by 20%. As lysosomes eliminate cellular waste (e.g., damaged organelles, misfolded proteins, and other cellular debris), this likely increases the elimination of the toxic aggregates that contribute to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s (particularly since DMSO also increases the permeability of cell membranes and hence the ability of cells to eliminate waste products). Likewise, by breaking down unneeded cellular materials, the energy they contain can be made available for cellular metabolism (which is often dysfunctional in neurodegenerative diseases).
•DMSO has also been proposed to prevent Alzheimer’s inhibits activation of inflammasomes, NLRP3, CASP1 and likewise due to DMSO binding the gene promoter for the antioxidant response element in the human apolipoprotein AI and doubling its transcriptional activity.
Cognitive Impairment and Dementia
Since many neurological disorders are linked to poor blood flow to the brain, previous traumas (e.g., concussions or microstrokes), the accumulation of misfolded proteins (e.g., this characterizes Alzheimer’s disease), or an autoimmune process (something DMSO also helps greatly with), it stands to reason that many cognitive disorders would respond to DMSO.
In turn, this is what we find, and that much in the same way DMSO reverses many other complications of aging (e.g., skin issue, hair loss, poor organ function) IV DMSO is one of the most effective anti-aging therapies for the brain (along with ultraviolet blood irradiation or improving the physiologic zeta potential). Likewise, IV DMSO is one of the only therapies I know of which can help challenging neurological diseases Parkinson’s or ALS (where in both cases, while not curative, typically halts the progression of the disease). In turn, I periodically come across anecdotes of DMSO consuming centenarians who have no cognitive impairment despite their age.
The animal research in this field is as follows:
•A study surgically modified rat carotid arteries to significantly reduce the amount of blood going to their brain. After 3 months, it was found that DMSO prevented both the neuronal damage and the significant loss of spatial memory and learning that otherwise resulted from that chronic loss of cerebral blood flow.
•In a similar study, rats 14 weeks old were subjected to either permanent bilateral carotid artery occlusion or sham occlusion (mimicking the chronic vascular impairments many experience with increasing age) and then tested the rats for visuospatial memory function. After 14 weeks, four rats who had shown persistent and severe memory impairment received DMSO and FDP for 7 days, which improved their memory by 54%, almost reaching the cognitive function of the controls. Unfortunately, this improvement was partially lost once DMSO-FDP were discontinued.1,2
•In rats, daily IV DMSO (for 2 weeks) counteracted memory impairment induced by intracerebroventricular STZ infusions, as shown by improved performance in behavioral and memory tests (e.g., Morris water maze). In a similar study, DMSO and Ginkgo biloba extract improved learning and memory in Alzheimer’s disease model rats (induced by β-amyloid 25-35 hippocampal injection), reducing escape latency and searching distance in the Morris water maze.
•0.01% DMSO was mixed with the drinking water of young (3-4 months) mice genetically engineered to have early onset Alzheimer’s. DMSO was found to mitigate the visual declines and ELM-RPE thickening within the retina seen in the prodromal phase of Alzheimer’s disease (with the benefits being comparable to those seen with R-carvedilol). Additionally improving that thickening was assumed to indicate DMSO enhanced the energy dependent transportation of water out of the eyes.
•In mice genetically engineered to have Alzheimer’s disease [AD], DMSO has been shown to increase neuronal density in the hippocampus (a brain region vulnerable to AD) and enhance their spatial memory and smell (while decreasing their anxiety), along with normalizing hippocampal hyperactivation and to modulate the NMDA receptor.
Note: DMSO has also been shown to greatly delay (by 48-98%) the paralysis caused by amyloid beta in C. elegans (one of the most popular organisms for aging research) and to extend the lifespan of C. elegans by 23.0-24.4%. The researchers attributed this delay in paralysis to DMSO modulating neurotransmission (e.g., DMSO is an acetylcholine esterase inhibitor, a therapeutic strategy also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease).
•In rats with rotenone-induced Parkinson’s, DMSO significantly improved the morphological integrity of pyramidal cells and Nissl bodies in the hippocampal CA1 and CA3 areas, counteracting the neuronal damage caused by rotenone. It also suppressed both inward (depolarizing) and outward (repolarizing) currents, enhanced tetanic depression responses, and strengthened inhibitory signaling in response to high-frequency stimulation (thereby counteracting the hyperexcitability and excessive activity induced by rotenone, protecting the hippocampus from excitotoxicity).
•In hamsters with scrapie infections, DMSO added to their water prolonged disease incubation time and delayed the accumulation of protease-resistant PrPSc in the brain. Additionally, much as DMSO helps amyloidosis, DMSO increased the excretion of protease-resistant PrP in the urine
•Lurcher mice are used to study olivary and cerebellar disorders because their Purkinje cells can’t survive (e.g., by 30 days of age their walking is grossly abnormal). When these mice received DMSO, it prevented the age-related deterioration of certain cognitive functions (e.g., memory and spatial learning abilities)
•A nasal insulin DMSO spray developed for treating Alzheimers, while never tested for clinical improvements, in rats was found to deliver insulin throughout the brain within an hour have no signs of toxicity.1,2
Most importantly, these results have been replicated in humans:
•18 patients with probable Alzheimer’s were treated with DMSO and tested regularly for nine months, with great improvements being noted after only three months of treatment, and becoming especially noticeable after six months of treatment. Areas of improvement included memory, concentration, and communication alongside a significant decrease of disorientation in time and space.
•Another study evaluated 104 elderly adults with organic brain disease due to cerebrovascular diseases (e.g., a previous stroke, cerebral embolism or a hardening of the arteries of the brain), a previous head injury, senility, or degenerative disease (e.g., Parkinson’s, hyperthyroidism or epilepsy). They received two DMSO mixes, Merinex (DMSO with amino acids) and Ipran (DMSO with vasoactive substances), typically alternating between the two, and for the majority of the time as an injection, and a minority of the time orally (with the fastest results occurred if both routes were used simultaneously), all of which resulted in remarkable improvements. To quote the author:
The DMSO aminoacid therapy is undoubtedly valuable in the treatment of numerous organic cerebral diseases. At the same time, thanks to the improved cerebral blood irrigation achieved by DMSO used in combination with vasoactive substances, a highly favorable effect on the psychic and somatic functions of senile patients was achieved.
Note: another study found Merinex treated patients with mood and anxiety disorders.
•A Chilean study evaluated 100 patients with cerebrovascular diseases (e.g., a previous stroke, cerebral embolism, or a hardening of the arteries of the brain), many of whom were senile, that received DMSO orally and through intramuscular injections over the course of 50 days. There it was noted that their coronary heart disease (i.e., atherosclerosis) and high blood pressure had a good improvement in 74.35% of DMSO recipients, a fair response in 21.77%, and no response for 3.88%. The neurologists overseeing these patients remarked that:
“Recovery from the general symptoms was positive; there were favorable changes which were reflected in a feeling of well being, the recovery of agility, changes of mood from depressed to gay, improvement of sleeping, and clearer speech. As regards the ‘focal’ results, accelerated recovery from hemiplegia and hemiparesia was registered. A speedier recovery of speech in cases of defined or indicated aphasia took place.”
Psychiatric Conditions
Another one of my favorite therapies, ultraviolet blood irradiation, essentially works by increasing circulation throughout the body, decreasing inflammation, and reawakening cells that have entered a dormant state (before they die). In turn, since these issues underlies so many different disease processes, a vast body of literature demonstrates its remarkable efficacy for a wide range of conditions, including psychiatric ones. As DMSO also essentially does these three things, some data has accumulated on its value in psychiatry.
•In 17 patients (ages 28-55 years) with chronic depression (for at least 5-20 years) that did not respond to antidepressant therapy whose most recent depressive episode lasted 8 months to 2 years, DMSO was able to treat their depression. Specifically, the existing basic antidepressant therapy (amythriptilin, pirasidol, anafranil), was combined with 1ml 50% oral DMSO and taken three times a day, resulting in 14 (82.3%) of the patients having a resolution of their depression which persisted for the 1-4 years of follow-up each patient received.
•In a study at a Peruvian psychiatric hospital, 42 patients (25 schizophrenics, 4 manic depressive psychotics, 4 alcoholic psychotics, 4 compulsive-obsessive neurotics and 5 patients with severe anxiety) were taken off all their medications then given 2-5 intramuscular injections each day (with more given to the most psychotic patients) and compared to 16 controls receiving standard care.
Of the schizophrenic, all 14 of the acute cases experienced a rapid and dramatic improvement (particularly in their agitation—especially for the catatonic-paranoid patients), with all being discharged within 45 days (three having a complete recovery 15 days after admission) and not having a recurrence. To quote one of them:
“I have been out of my mind. I don’t know what happened to me. I wonder what my children are going to say.”
Of the 11 chronic schizophrenics, 4 periodically needed hospitalization and had a complete remission following DMSO (allowing them to be discharged much faster than normal), and in those who later relapsed, there was again a positive response to DMSO. The remaining 7 were more severe cases (e.g., they had been hospitalized for over 6 years and failed years of therapies) and experienced an improvement from DMSO, but it was not enough to leave the hospital.
Note: results like this (I’ve seen similar ones with other therapies as well) lead me to believe that the existing understanding of schizophrenia is extremely incomplete. To further support that contention, this author also shared a case of a severely delusional paranoid schizophrenic responding to DMSO.
The 4 manic-depressive psychotics (who were in the manic phase, averaging 15 days of psychomotor agitation) rapidly calmed down and lost their mania after DMSO (with their recovery being much faster than what they’d previously experienced from conventional therapy).
The 4 alcoholic psychotics (2 with hallucinations and 2 with delirium tremens) had previously been hospitalized for these issues. They rapidly responded to DMSO, with restlessness improving in the first few days while the hallucinations took longer.
The remaining patients (obsessive-compulsive neurosis and severe anxiety) also had a good response to DMSO (e.g., they were calmer, ideas did not upset them as before, they were able to act in a more spontaneous way, and they were able to overcome their obsessive compulsions).
Note: in another 1970 study, the DMSO amino acid mix was used to treat depressed neurotics.
Lastly, numerous rat studies have found DMSO prevents the adverse physiologic effects of chronic emotional painful stress (EPS):
•In one, DMSO combined with vitamin E showed potent antistress effects, preventing stress-induced hypertension, autonomic nervous system reactivity issues, and behavioral changes in the open field test while also reducing free-radical oxidation products, increased superoxide scavenging activity in brain and serum, elevated brain phospholipid levels, and lowered cholesterol and the cholesterol/phospholipid ratio.
•In another, DMSO counteracted EPS induced increased transferrin and decreased ceruloplasmin/transferrin ratio and decreased superoxide-scavenging activity.1,2
•In another, DMSO prevented EPS induced behavioral disturbances, gastric ulcers, and hypertension, while normalizing cardiovascular and autonomic nervous system functions. DMSO also reduced oxidative stress (e.g., reducing lipid peroxidation and MDA levels along with increasing SOD activity by 29-43% in the brain and 18-45% in serum.1,2
Developmental Disabilities
One of the most remarkable effects of DMSO is its effects on developmental disabilities. For example, at a hearing Congress convened to (unsuccessfully) pressure the FDA to end its embargo on DMSO, testimony was given of a child with Down Syndrome (classically considered incurable) having a miraculous response to DMSO.
There, Melody Clark, was discussed, who at 11 months (unable to stand or walk, had protruding tongue and all the classic Down Syndrome symptoms) was started on DMSO. She improved and at eight years of age, was able to walk, run, talk, read, and spell almost normally—something her teachers had never seen in another child with Down Syndrome. Specifically, she functioned at a second-grade level (with verbal competency and excelling in arithmetic), could engage in normal physical activities, and was very socially minded (allowing her to be quite popular with her peers).
In short, she transitioned from a vegetative existence (e.g., initially she couldn’t stand and her eyes were constantly out of focus) to having a minor developmental disability.
Note: Melody’ dentist provided testimony that her mouth and palate had largely normalized (another common issue in Down Syndrome), something he had never seen occur in this patient population.
Two other similar cases have also been reported:
•At 10 months of age, Bronwyn Nash (who had Down Syndrome) was frail and unable to gain weight, so her mother started her on DMSO. She began gaining weight and developed an increased awareness of the people and objects around her and then started reaching out to touch things. At 18 months, she was able to stand up, and then became able to get into her mother’s cupboards, started to feed herself, and held her water glass well. At the time a health journalist visited her at 28 months of age, she was an alert, cheerful little girl much enjoyed and well loved by her family and improving steadily.
•At 14, Billy King could walk and feed himself but had the mental capacity of a ten month old. He then began drinking milk with DMSO each morning, and two years later, had the mental capacity of a seven year old and began losing the characteristic Down "Syndrome appearance.
He continued to improve and was eventually able to hold a job in a Portland bookstore.
Note: another account of Billy King’s story has a different chronology (e.g., he started DMSO at 8 not 14, and also took the amino acid formula).
Research in turn exists to support these unbelievable anecdotes.
•In Oregon, 67 moderately or severely mentally disabled children (aged 4-17) with Down Syndrome were randomized to receive a high or low DMSO dose and then were compared to 23 similar children whose parents did not want them to receive an experimental drug. No side effects occurred and a dose dependent improvement was observed:
In Chile, 55 children with severe mental disability caused by Down syndrome (the oldest being 14) were given DMSO and amino acids by intramuscular injection or served as controls. The vials for injection consisted of DMSO along with gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), gamma amino beta hydroxybutyric acid (GABOB), and acetyl glutamine (with lower doses given to those under 3 1⁄2 years of age). The children’s development was then evaluated with Gessel scores and a massive improvement was seen in the DMSO group:
Note: this study (and the additional improvements that occurred) can be viewed here and here.
In Argentina, 13 mentally disabled children (5 severe cases, 4 moderate cases, and 4 mild ones), who did not have Down Syndrome, received a DMSO amino acid mixture (known as Merinex) three times a week by injection for 180 days (with periodic 15 day periods where the amino acids without DMSO were administered orally)
Note: other authors have reported young patients (and older ones) with learning difficulties, low intelligence, ADHD, anxiety disorders, epilepsy, nervousness, dyscalculia, dyslexia, exhaustion, and concentration problems all benefit from this protocol. Additionally, some have argued adding galactose to it enhances its efficacy.
In a 1969 study, 44 severely developmentally delayed children received the DMSO amino acid mix, with many experiencing a heightened capacity for learning in them in a relatively short time and over 70% having favorable responses such as a “increase of the IQ, an evident and accelerated progress in basic achievements, an overall improvement of intellectual capacity, evident progress in reading, writing, and mathematics, better coordination of movements and improved manual skill, and a decrease of behavioral problems," along with gaining better psychomotor control, no longer having anger for no reason, a general reduction of irritability, and a lessening of disobedience.
Another 1969 study gave the DMSO amino acid mixture for six months to 30 learning disabled children with language disorders (who did not have an accompanying neurological illness) and compared them to 20 controls, and observed it resulted in:
1. Disappearance of mental lethargy.
2. Evidence of sensorial reactions.
3. Disappearance of automatic movements.
4. Disappearance of inertia, passivity, and negativity.
5. Growing interest and initiative in tasks and activities.
6. Improvement of the physiognomic expression and of the spoken language.
7. Lucid activity, group contact, and disappearance of unprovoked aggressiveness.
8. Losing shyness and developing self-esteem.
9. Successful training to carry out chores, to do shopping, to eat, and to dress without help, etc.
10. Learning to read and to write and to do homework.
A 1976 Chile study gave DMSO and amino acids (GABA, GABOB, L-acetylglutamine, and arginine) to 15 children (under 3.5 years old) with Down Syndrome and compared them to 13 untreated controls. After 12 months of intensive treatment, per the Gesell Developmental Quotient, motor area average rose from 56 to 72, adaptive from 50 to 66, language from 52 to 58, and social from 40 to 64 (with many individuals improving >10 points, especially in motor, adaptive, and social domains), while controls remained largely unchanged. Physical improvements included reduced macroglossia, better facial expressiveness, increased muscle tone/coordination, and postural changes in treated children. During the subsequent 6-month maintenance phase (to 18 months total), treated children’s gains were largely maintained or slightly increased (e.g., motor to 74, adaptive to 69, social to 67), with no significant regression and only minor isolated losses (e.g., in language for a few), whereas controls showed no progress or slight declines. The authors noted no significant adverse effects and concluded that early intervention appeared beneficial for neuronal stimulation and development.1,2
One author reported on an Argentinian study (I could not find) conducted by this physician. where 18 children with Down syndrome received DMSO and amino acids and were compared to 91 controls, and to quote the author this resulted in:
a tendency towards accelerated maturity in the children treated, with marked progress in language integration; this could be established in statistically significant degrees in the children treated
Additionally, this study, and this study, also found the DMSO amino acid mixture benefitted developmentally disabled children.
Note: a different book authored by the leading DMSO researcher reported that veterinarian Jack Metcalf had found horses developmentally disabled at birth (to the point they can’t nurse) once given IV DMSO three times daily regain the ability to nurse and that DMSO accelerates their overall development.
DMSO in Context
Because DMSO had the fortune to be discovered at a time when there was still an unbridled enthusiasm within the scientific community to investigate an unorthodox idea (something which has largely disappeared now because career scientists are so dependent upon not rocking the boat to ensure a lifetime supply of research grants) and it fell into the right people’s lap (exceptionally talented, ethical and driven physicians who’d earned the support of their superiors) the scientific community rallied behind it and published thousands of papers on DMSO.
Nonetheless, the FDA was still able to squelch it, and all of the research behind it (along with all the animals that were sacrificed to attain it) have been consigned to the dustbins of history. In the case of DMSO, this is particularly tragic because of how much suffering (and economic cost) many of the disorders discussed here create and the fact that decades of research and billions of research dollars have brought us no closer to solving them.
I thus made the decision to present this in a neutral tone and do my best to accurately present that science behind DMSO (which has required hundreds of hours of work) so I could give DMSO the best chance of flourishing now and helping those it could help—but in truth—words cannot begin to express my disdain over how DMSO was treated or the human cost of the callous bureaucratic dictates which have kept it from being adopted within the medical system (a sentiment I believe will be shared by many of you). For example, this is what Pierre Kory said after I asked him to review this article:
In the over 15 years I spent running ICU’s managing many kinds of brain injuries, strokes and bleeds, it both infuriates and saddens me to know of an intervention that could’ve helped so many of the hundreds of devastating neurological illnesses that I valiantly and often largely unsuccessfully tried to reverse to health. The therapeutic strategies that I had to rely on like tPa were often quite limited in impact or introduced major risks to the patient.
Note: the reason this project has taken so long is because even here, I only touched the tip of the iceberg, and there are still many other paradigm shifting uses for DMSO (e.g., it is a safe and effective painkiller, it treats both acute musculoskeletal injuries and chronic ones creating significant physical impairment, and it provides a way to treat many other challenging conditions that still do not have an effective therapy within the standard of care). In turn my hope is provide the rest of the DMSO in the near future.
As so much has been forgotten about DMSO, few are aware of its intravenous applications (even its proponents). In the final part of this article, I will discuss everything we know on the subject (e.g., where to procure it, what supplies to use, how to dose it) and the non-IV protocols we’ve used for strokes (since IV DMSO was often not feasible in those situations) and other traumatic injuries both at the time of injury and afterward for recovery (e.g., IV DMSO is one of the best options for stroke rehabilitation).